Tissue-resident, extravascular Ly6c- monocytes are critical for inflammation in the synovium
- PMID: 37204925
- PMCID: PMC10697497
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112513
Tissue-resident, extravascular Ly6c- monocytes are critical for inflammation in the synovium
Abstract
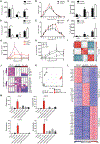
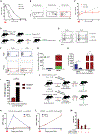
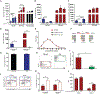
Monocytes are abundant immune cells that infiltrate inflamed organs. However, the majority of monocyte studies focus on circulating cells, rather than those in tissue. Here, we identify and characterize an intravascular synovial monocyte population resembling circulating non-classical monocytes and an extravascular tissue-resident monocyte-lineage cell (TR-MC) population distinct in surface marker and transcriptional profile from circulating monocytes, dendritic cells, and tissue macrophages that are conserved in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. TR-MCs are independent of NR4A1 and CCR2, long lived, and embryonically derived. TR-MCs undergo increased proliferation and reverse diapedesis dependent on LFA1 in response to arthrogenic stimuli and are required for the development of RA-like disease. Moreover, pathways that are activated in TR-MCs at the peak of arthritis overlap with those that are downregulated in LFA1-/- TR-MCs. These findings show a facet of mononuclear cell biology that could be imperative to understanding tissue-resident myeloid cell function in RA.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; arthritis; macrophages; monoyctes.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Guilliams M, Mildner A, and Yona S (2018). Developmental and functional heterogeneity of monocytes. Immunity 49, 595–613. - PubMed
-
- Mildner A, Schönheit J, Giladi A, David E, Lara-Astiaso D, Lorenzo-Vivas E, Paul F, Chappell-Maor L, Priller J, Leutz A, et al. (2017). Genomic characterization of murine monocytes reveals C/EBPbeta transcription factor dependence of Ly6C(−) cells. Immunity 46, 849–862.e7. 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.04.018. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- I01 CX001777/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 AR080513/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AR074902/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG049665/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI135964/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AR007611/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL153312/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA060553/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI163742/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL145478/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147290/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 HL135124/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR075423/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL154998/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- KL2 TR001424/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL147575/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL134375/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

