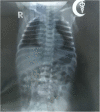
A case of Pierre Robin syndrome in a child with no soft palate and complications from pneumonia in Bangladesh
- PMID: 37205152
- PMCID: PMC10185733
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.7350
A case of Pierre Robin syndrome in a child with no soft palate and complications from pneumonia in Bangladesh
Abstract
Key clinical message: Children with Pierre Robin syndrome (PRS) often have trouble breathing and eating as soon as they are born. If conservative therapy fails to alleviate airway obstruction, surgical surgery may be considered. Patients with PRS require multidisciplinary approaches for treatment.
Abstract: Pierre Robin syndrome is a common craniofacial abnormality that causes glossoptosis and blockage of the upper airway. This renders it difficult to feed, which leads to severe malnutrition. This condition is also often marked by an absence of a soft palate. We mention a newborn with Pierre Robin syndrome with the absence of a soft palate and pneumonia complications, whose impending respiratory failure was treated successfully. To solve the complex problems that these babies and their families are facing, a multidisciplinary approach is needed.
Keywords: Pierre Robin syndrome; congenital defects; feeding problem; micrognathia; pediatrics; pneumonia; soft palate.
© 2023 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tongue lip adhesion (TLA) in the management of airway obstruction and feeding in Pierre Robin sequence, a case report.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024 Aug;121:109932. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2024.109932. Epub 2024 Jun 22. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38936141 Free PMC article.
-
Case report of Pierre Robin sequence with severe upper airway obstruction who was rescued by fiberoptic nasotracheal intubation.BMC Anesthesiol. 2017 Mar 14;17(1):43. doi: 10.1186/s12871-017-0336-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2017. PMID: 28288578 Free PMC article.
-
Pierre robin sequence.Semin Plast Surg. 2012 May;26(2):76-82. doi: 10.1055/s-0032-1320065. Semin Plast Surg. 2012. PMID: 23633934 Free PMC article.
-
Management of cleft palate among patients with Pierre Robin sequence.Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023 Sep;61(7):475-481. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2023.06.003. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2023. PMID: 37453893 Review.
-
Pierre Robin sequence: Management of respiratory and feeding complications during the first year of life in a tertiary referral centre.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Aug;79(8):1206-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.05.012. Epub 2015 Jun 6. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 26092549 Review.
Cited by
-
Syndromic Piere Robbin Sequence- A Rare Presentation in Association with Multiple Heart Defects and Type III Stickler Syndrome.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024 Feb;76(1):1325-1327. doi: 10.1007/s12070-023-04307-x. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2024. PMID: 38440550 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . The Global Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization; 2008.
-
- Parmar A, Rathod SP, Patel SV, Patel SM. A study of congenital anomalies in newborn. NJIRM. 2010;1(1):13‐17.
-
- Tomatır AG, Demirhan H, Sorkun HÇ, et al. Major congenital anomalies: a five‐year retrospective regional study in Turkey. Genet Mol Res. 2009;8:19‐27. - PubMed
-
- Baujat G, Faure C, Zaouche A, Viarme F, Couly G, Abadie V. Oroesophageal motor disorders in Pierre Robin syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2001;32(3):297‐302. - PubMed
-
- Guven DG, Senses DA, Subasi B, Yaman H. Absence of the epiglottis in an infant with Pierre Robin sequence. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2011;6(3):137‐139.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources