This is a preprint.
Bivalent and Monovalent SARS-CoV-2 Variant Vaccine Boosters Improve coverage of the known Antigenic Landscape: Results of the COVID-19 Variant Immunologic Landscape (COVAIL) Trial
- PMID: 37205592
- PMCID: PMC10187423
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2653179/v1
Bivalent and Monovalent SARS-CoV-2 Variant Vaccine Boosters Improve coverage of the known Antigenic Landscape: Results of the COVID-19 Variant Immunologic Landscape (COVAIL) Trial
Update in
-
Comparison of bivalent and monovalent SARS-CoV-2 variant vaccines: the phase 2 randomized open-label COVAIL trial.Nat Med. 2023 Sep;29(9):2334-2346. doi: 10.1038/s41591-023-02503-4. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Nat Med. 2023. PMID: 37640860 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
Abstract
Vaccine protection against COVID-19 wanes over time and has been impacted by the emergence of new variants with increasing escape of neutralization. The COVID-19 Variant Immunologic Landscape (COVAIL) randomized clinical trial (clinicaltrials.gov NCT05289037) compares the breadth, magnitude and durability of antibody responses induced by a second COVID-19 vaccine boost with mRNA (Moderna mRNA-1273 and Pfizer-BioNTech BNT162b2), or adjuvanted recombinant protein (Sanofi CoV2 preS DTM-AS03) monovalent or bivalent vaccine candidates targeting ancestral and variant SARS-CoV-2 spike antigens (Beta, Delta and Omicron BA.1). We found that boosting with a variant strain is not associated with loss in neutralization against the ancestral strain. However, while variant vaccines compared to the prototype/wildtype vaccines demonstrated higher neutralizing activity against Omicron BA.1 and BA.4/5 subvariants for up to 3 months after vaccination, neutralizing activity was lower for more recent Omicron subvariants. Our study, incorporating both antigenic distances and serologic landscapes, can provide a framework for objectively guiding decisions for future vaccine updates.
Figures


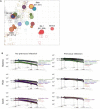
References
-
- WHO. World Health Organization, Weekly Operational Update on COVID-19. https://wwwwhoint/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situation-... 2020a;Accessed January 20, 2022..
-
- JHU. COVID-19 Dashboard, Center for Systems Science and Engineering (CCSE) at Johns Hopkins University (JHU). https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html.;Accessed January 20, 2022.
Publication types
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

