Policies and socioenvironmental dynamics for ecosystem management
- PMID: 37206646
- PMCID: PMC10189367
- DOI: 10.1016/j.mex.2023.102205
Policies and socioenvironmental dynamics for ecosystem management
Abstract
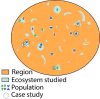
The continuous loss of biodiversity has extended the Convention on Biological Diversity's target towards safeguarding 30% of the planet by 2030 with some form of protected area management. This is a challenge, considering the poor compliance of the Aichi Biodiversity Targets reported in several assessments, and that 37% of the remaining unprotected natural areas are inhabited by indigenous and local communities. Modern conservation policies tend to convert areas destined for protection into complex socioecological landscapes, so it is critical to develop policies capable of establishing long-term harmonious relations between local societies and their environments. Despite the fundamental importance of defining this interrelation, methodologies for evaluating it are still unclear. We propose a method for assessing the outcome of policies in socioenvironmental practices based on a historical-political ecology analysis of a region, the construction of socioenvironmental scenarios, and comparing populations scattered through the study area. Each "scenario" is a relation between nature and society after a shift in public policies. Conservation scientists, environmental managers, and policymakers can use this methodology to assess old policies, design new ones, or map the socioenvironmental dynamics in their area of interest. Here, we detail this approach and illustrate its application in the coastal wetlands of Mexico. The method can be outlined as follows:•Deduce socioenvironmental epochs for a region by analysing its historical political ecology.•Analyse the socioenvironmental dynamics in selected case studies scattered through the region.•Use the resulting scenarios as conceptual bridges between internal policies and current socioenvironmental dynamics.
Keywords: Community-based lands; Conservation; Development; Governance; Historical political ecology; Local production-based management; Method for relating domestic policies and socioenvironmental dynamics; Socioenvironmental evaluation.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relations that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Convention on Biological Diversity. (2021). First draft of the post 2020 global biodiversity framework. https://www.cbd.int/doc/c/abb5/591f/2e46096d3f0330b08ce87a45/wg2020-03-0.... Accessed 04 May 2023.: Convention on Biological Diversity, UN environment programme.
-
- Convention on Biological Diversity . UNEP; 2020. Analysis of the Contribution of Targets Established By Parties and Progress Towards the Aichi Biodiversity Targets’.CBD/SBI/3/2/Add.2 24-29 Aug. 2020.
-
- Koh N.S., Ituarte-Lima C., Hahn T. Mind the compliance gap: how insights from international human rights mechanisms can help to implement the convention on biological diversity. Transnatl. Environ. Law. 2022;11(1):39–67.
-
- Visconti P., Butchart S.H., Brooks T.M., Langhammer P.F., Marnewick D., Vergara S., Watson J.E. Protected area targets post-2020. Science. 2019;364(6437):239–241. - PubMed
-
- Büscher B., Fletcher R., Brockington D., Sandbrook C., Adams W.M., Campbell L., Corson C., Dressler W., Duffy R., Gray N. Half-earth or whole earth? radical ideas for conservation, and their implications. Oryx. 2017;51(3):407–410. doi: 10.1017/S0030605316001228. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources