SH2db, an information system for the SH2 domain
- PMID: 37207333
- PMCID: PMC10320075
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad420
SH2db, an information system for the SH2 domain
Abstract
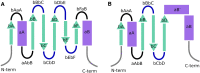
SH2 domains are key mediators of phosphotyrosine-based signalling, and therapeutic targets for diverse, mostly oncological, disease indications. They have a highly conserved structure with a central beta sheet that divides the binding surface of the protein into two main pockets, responsible for phosphotyrosine binding (pY pocket) and substrate specificity (pY + 3 pocket). In recent years, structural databases have proven to be invaluable resources for the drug discovery community, as they contain highly relevant and up-to-date information on important protein classes. Here, we present SH2db, a comprehensive structural database and webserver for SH2 domain structures. To organize these protein structures efficiently, we introduce (i) a generic residue numbering scheme to enhance the comparability of different SH2 domains, (ii) a structure-based multiple sequence alignment of all 120 human wild-type SH2 domain sequences and their PDB and AlphaFold structures. The aligned sequences and structures can be searched, browsed and downloaded from the online interface of SH2db (http://sh2db.ttk.hu), with functions to conveniently prepare multiple structures into a Pymol session, and to export simple charts on the contents of the database. Our hope is that SH2db can assist researchers in their day-to-day work by becoming a one-stop shop for SH2 domain related research.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures




References
-
- Koch C., Anderson D., Moran M., Ellis C., Pawson T.. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science. 1991; 252:668–674. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T., Gish G.D., Nash P.. SH2 domains, interaction modules and cellular wiring. Trends Cell Biol. 2001; 11:504–511. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

