Study protocol of the InterVitaminK trial: a Danish population-based randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled trial of the effects of vitamin K (menaquinone-7) supplementation on cardiovascular, metabolic and bone health
- PMID: 37208133
- PMCID: PMC10201225
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-071885
Study protocol of the InterVitaminK trial: a Danish population-based randomised double-blinded placebo-controlled trial of the effects of vitamin K (menaquinone-7) supplementation on cardiovascular, metabolic and bone health
Abstract
Introduction: Vitamin K has been suggested to have protective effects against progression of vascular calcification and development of cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, few well-powered randomised controlled trials have examined whether vitamin K prevents progression of vascular calcification in individuals from the general population. The aim of the InterVitaminK trial is to investigate the effects of vitamin K supplementation (menaquinone-7, MK-7) on cardiovascular, metabolic, respiratory and bone health in a general ageing population with detectable vascular calcification.
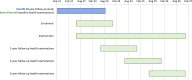
Methods and analysis: The InterVitaminK trial is a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled, trial. A total of 450 men and women aged 52-82 years with detectable coronary artery calcification (CAC), but without manifest CVD, will be randomised (1:1) to receive daily MK-7 (333 µg/day) or placebo tablets for 3 years. Health examinations are scheduled at baseline, and after 1, 2 and 3 years of intervention. Health examinations include cardiac CT scans, measurements of arterial stiffness, blood pressure, lung function, physical function, muscle strength, anthropometric measures, questionnaires on general health and dietary intake, and blood and urine sampling. The primary outcome is progression of CAC from baseline to 3-year follow-up. The trial has 89% power to detect a between-group difference of at least 15%. Secondary outcomes are bone mineral density, pulmonary function and biomarkers of insulin resistance.
Ethics and dissemination: Oral MK-7 supplementation is considered safe and has not been found to cause severe adverse events. The Ethical Committee of the Capital Region (H-21033114) approved the protocol. Written informed consent is obtained from all participants and the trial is conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki II. Both negative and positive findings will be reported.
Trial registration number: NCT05259046.
Keywords: CARDIOLOGY; Calcium & bone; General endocrinology; NUTRITION & DIETETICS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: FBK, SMT and AL have received funds and tablets for the trial from Kappa Bioscience AS. AL discloses the application of a patent on vitamin K on lung function for prognostic and therapeutic purposes. Aside from this, the authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
