Quantification of virus-infected cells using RNA FISH-Flow
- PMID: 37209094
- PMCID: PMC10209735
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2023.102291
Quantification of virus-infected cells using RNA FISH-Flow
Abstract
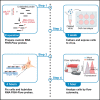
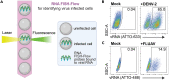
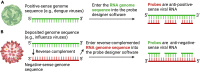
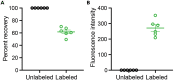
We present a protocol to detect cells that have been infected by RNA viruses. The method, RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization flow cytometry (RNA FISH-Flow), uses 48 fluorescently labeled DNA probes that hybridize in tandem to viral RNA. RNA FISH-Flow probes can be synthesized to match any RNA virus genome, in either sense or anti-sense, enabling detection of genomes or replication intermediates within cells. Flow cytometry enables high-throughput analysis of infection dynamics within a population at the single cell level. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Warren et al. (2022).1.
Keywords: In Situ Hybridization; Microbiology; Molecular Biology.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests S.L.S. and Q.Y. are co-founders of Darwin Biosciences.
Figures
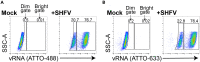
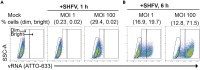
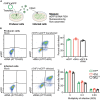
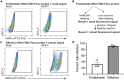
References
-
- Warren C.J., Yu S., Peters D.K., Barbachano-Guerrero A., Yang Q., Burris B.L., Worwa G., Huang I.-C., Wilkerson G.K., Goldberg T.L., et al. Primate hemorrhagic fever-causing arteriviruses are poised for spillover to humans. Cell. 2022;185:3980–3991.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2022.09.022. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

