Primary tumor resection or systemic treatment as palliative treatment for patients with isolated synchronous colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases in a nationwide cohort study
- PMID: 37209222
- PMCID: PMC10338565
- DOI: 10.1007/s10585-023-10212-y
Primary tumor resection or systemic treatment as palliative treatment for patients with isolated synchronous colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases in a nationwide cohort study
Abstract
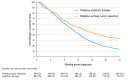
Limited data are available to guide the decision-making process for clinicians and their patients regarding palliative treatment options for patients with isolated synchronous colorectal cancer peritoneal metastases (CRC-PM). Therefore, the aim of this study is to analyze the outcome of the different palliative treatments for these patients. All patients diagnosed with isolated synchronous CRC-PM between 2009 and 2020 (Netherlands Cancer Registry) who underwent palliative treatment were included. Patients who underwent emergency surgery or curative intent treatment were excluded. Patients were categorized into upfront palliative primary tumor resection (with or without additional systemic treatment) or palliative systemic treatment only. Overall survival (OS) was compared between both groups and multivariable cox regression analysis was performed. Of 1031 included patients, 364 (35%) patients underwent primary tumor resection and 667 (65%) patients received systemic treatment only. Sixty-day mortality was 9% in the primary tumor resection group and 5% in the systemic treatment group (P = 0.007). OS was 13.8 months in the primary tumor resection group and 10.3 months in the systemic treatment group (P < 0.001). Multivariable analysis showed that primary tumor resection was associated with improved OS (HR 0.68; 95%CI 0.57-0.81; P < 0.001). Palliative primary tumor resection appeared to be associated with improved survival compared to palliative systemic treatment alone in patients with isolated synchronous CRC-PM despite a higher 60-day mortality. This finding must be interpreted with care as residual bias probably played a significant role. Nevertheless, this option may be considered in the decision-making process by clinicians and their patients.
Keywords: Colorectal cancer; Palliative primary tumor resection; Palliative systemic treatment; Peritoneal metastases.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Koopman reported having an advisory role for Nordic Farma, Merck-Serono, Pierre Fabre, Servier, Institutional scientific grants from Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck, Personal Genome Diagnostics (PGDx), Pierre Fabre, Roche, Sirtex, Servier. Dr. de Wilt reported an unrestricted research grant from Medtronic and Roche, outside the submitted work, paid to the institute. Dr. de Hingh reported an unrestricted research grant from RanD/QPS and Roche, outside the submitted work, paid to the institute. For the remaining authors none were declared.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organisation. Global Cancer Observatory. Accessed April 1 (2022) https://gco.iarc.fr/today/home
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

