Hippocampus long-axis specialization throughout development: A meta-analysis
- PMID: 37209288
- PMCID: PMC10318218
- DOI: 10.1002/hbm.26340
Hippocampus long-axis specialization throughout development: A meta-analysis
Abstract
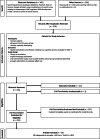
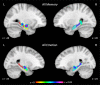
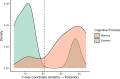
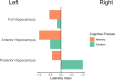
The human adult hippocampus can be subdivided into the head, or anterior hippocampus and its body and tail, or posterior hippocampus, and a wealth of functional differences along the longitudinal axis have been reported. One line of literature emphasizes specialization for different aspects of cognition, whereas another emphasizes the unique role of the anterior hippocampus in emotional processing. While some research suggests that functional differences in memory between the anterior and posterior hippocampus appear early in development, it remains unclear whether this is also the case for functional differences in emotion processing. The goal of this meta-analysis was to determine whether the long-axis functional specialization observed in adults is present earlier in development. Using a quantitative meta-analysis, long-axis functional specialization was assessed using the data from 26 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies, which included 39 contrasts and 804 participants ranging in age from 4 to 21 years. Results indicated that emotion was more strongly localized to the anterior hippocampus, with memory being more strongly localized to the posterior hippocampus, demonstrating long-axis specialization with regard to memory and emotion in children similar to that seen in adults. An additional analysis of laterality indicated that while memory was left dominant, emotion was processed bilaterally.
Keywords: development; fMRI; hippocampus; long-axis specialization; meta-analysis.
© 2023 The Authors. Human Brain Mapping published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bartha‐Doering, L. , Novak, A. , Kollndorfer, K. , Kasprian, G. , Schuler, A. L. , Berl, M. M. , Fischmeister, F. P. S. , Gaillard, W. D. , Alexopoulos, J. , Prayer, D. , & Seidl, R. (2018). When two are better than one: Bilateral mesial temporal lobe contributions associated with better vocabulary skills in children and adolescents. Brain and Language, 184(June), 1–10. 10.1016/j.bandl.2018.06.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

