Transcriptome wide functional analysis of HBx expressing human hepatocytes stimulated with endothelial cell cross-talk
- PMID: 37209778
- PMCID: PMC7615065
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ygeno.2023.110642
Transcriptome wide functional analysis of HBx expressing human hepatocytes stimulated with endothelial cell cross-talk
Abstract
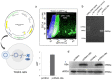
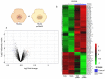
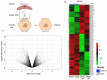
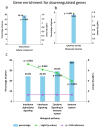
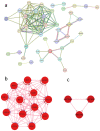
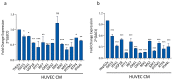
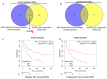
Identification of genes dysregulated during the hepatitis B virus (HBV)-host cell interaction adds to the understanding of underlying molecular mechanisms and aids in discovering effective therapies to improve prognosis in hepatitis B virus (HBV)-infected individuals. Through bioinformatics analyses of transcriptomics data, this study aimed to identify potential genes involved in the cross-talk of human hepatocytes expressing the HBV viral protein HBx with endothelial cells. Transient transfection of HBV viral gene X (HBx) was performed in THLE2 cells using pcDNA3 constructs. Through mRNA Sequencing (RNA Seq) analysis, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified. THLE2 cells transfected with HBx (THLE2x) were further treated with conditioned medium from cultured human umbilical vein derived endothelial cells (HUVEC-CM). Gene Ontology (GO) enrichment analysis revealed that interferon and cytokine signaling pathways were primarily enriched for the downregulated DEGs in THLE2x cells treated with HUVEC-CM. One significant module was selected following protein-protein interaction (PPI) network generation, and thirteen hub genes were identified from the module. The prognostic values of the hub genes were evaluated using Kaplan-Meier (KM) plotter, and three genes (IRF7, IFIT1, and IFITM1) correlated with poor disease specific survival (DSS) in HCC patients with chronic hepatitis. A comparison of the DEGs identified in HUVEC-stimulated THLE2x cells with four publicly available HBV-related HCC microarray datasets revealed that PLAC8 was consistently downregulated in all four HCC datasets as well as in HUVEC-CM treated THLE2x cells. KM plots revealed that PLAC8 correlated with worse relapse free survival and progression free survival in HCC patients with hepatitis B virus infection. This study provided molecular insights which may help develop a deeper understanding of HBV-host stromal cell interaction and open avenues for future research.
Keywords: Conditioned medium; Endothelial cells; HBV X gene (HBx); HUVEC; Hepatitis B; THLE2; Transcriptome.
Copyright © 2023. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
miR-106b promotes cancer progression in hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jun 14;22(22):5183-92. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i22.5183. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27298561 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of B7-H4 and hepatitis B virus X in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 May 14;22(18):4538-46. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i18.4538. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 27182163 Free PMC article.
-
[Bioinformatics analysis of core differentially expressed genes in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 21;34(5):507-513. doi: 10.16250/j.32.1374.2021292. Zhongguo Xue Xi Chong Bing Fang Zhi Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36464255 Chinese.
-
The Multiple Roles of Hepatitis B Virus X Protein (HBx) Dysregulated MicroRNA in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HBV-HCC) and Immune Pathways.Viruses. 2020 Jul 10;12(7):746. doi: 10.3390/v12070746. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 32664401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B virus, HBx mutants and their role in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug 14;20(30):10238-48. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i30.10238. World J Gastroenterol. 2014. PMID: 25132741 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical Utility of IFIT Proteins in Human Malignancies.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 11;13(6):1435. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061435. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Upregulated enhancer of rudimentary homolog promotes epithelial‑mesenchymal transition and cancer cell migration in lung adenocarcinoma.Mol Med Rep. 2024 Jan;29(1):9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2023.13132. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 37997813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Schweitzer A, Horn J, Mikolajczyk RT, Krause G, Ott JJ. Lancet. 10003. Vol. 386. Elsevier; 2015. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013; pp. 1546–1555. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB, Rudolph KL. Hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology. 2007 Jun;132(7):2557–2576. - PubMed
-
- Breiner KM, Schaller H, Knolle PA. Hepatology. 4. Vol. 34. Wiley Online Library; 2001. Endothelial cell–mediated uptake of a hepatitis B virus: a new concept of liver targeting of hepatotropic microorganisms; pp. 803–808. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

