Postoperative effect of sufentanil preemptive analgesia combined with psychological intervention on breast cancer patients
- PMID: 37210488
- PMCID: PMC10199579
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-023-02143-8
Postoperative effect of sufentanil preemptive analgesia combined with psychological intervention on breast cancer patients
Abstract
Objectives: To explore the postoperative effects of sufentanil preemptive analgesia combined with psychological intervention on breast cancer patients undergoing radical surgery.
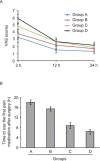
Methods: 112 female breast cancer patients aged 18-80 years old who underwent radical surgery by the same surgeon were randomly divided into 4 groups, and there were 28 patients in each group. Patients in group A were given 10 µg sufentanil preemptive analgesia combined with perioperative psychological support therapy (PPST), group B had only 10 µg sufentanil preemptive analgesia, group C had only PPST, and group D were under general anesthesia with conventional intubation. Visual analogue scoring (VAS) was used for analgesic evaluation at 2, 12 and 24 h after surgery and compared among the four groups by ANOVA method.
Results: The awakening time of patients in group A or B was significantly shorter than that in group C or D, and the awakening time in group C was significantly shorter than that in group D. Moreover, patients in group A had the shortest extubation time, while the group D had the longest extubation time. The VAS scores at different time points showed significant difference, and the VAS scores at 12 and 24 h were significantly lower than those at 2 h (P < 0.05). The VAS scores and the changing trend of VAS scores were varied among the four groups (P < 0.05). In addition, we also found that patients in group A had the longest time to use the first pain medication after surgery, while patients in group D had the shortest time. But the adverse reactions among the four groups showed no difference.
Conclusions: Sufentanil preemptive analgesia combined with psychological intervention can effectively relieve the postoperative pain of breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer patients; Preoperative analgesia; Psychological intervention; Sufentanil.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prospective investigation of intravenous patient-controlled analgesia with hydromorphone or sufentanil: impact on mood, opioid adverse effects, and recovery.BMC Anesthesiol. 2018 Apr 10;18(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s12871-018-0500-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2018. PMID: 29636011 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The continuous epidural infusion of ropivacaine 0.1% with 0.5 microg x mL(-1) sufentanil provides effective postoperative analgesia after total hip replacement: a pilot study.Can J Anaesth. 2003 Jun-Jul;50(6):580-5. doi: 10.1007/BF03018644. Can J Anaesth. 2003. PMID: 12826550 Clinical Trial.
-
Intravenous lidocaine simultaneously infused with sufentanil to accelerate gastrointestinal function recovery in patients after thoracolumbar surgery: a prospective, randomized, double-blind controlled study.Eur Spine J. 2023 Jan;32(1):313-320. doi: 10.1007/s00586-022-07456-9. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Eur Spine J. 2023. PMID: 36394651 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of Dezocine and Sufentanil on Th1/Th2 Balance in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Surgery.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Dec 2;15:4925-4938. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S326891. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34880602 Free PMC article.
-
[Effects of S(+)-ketamine combined with sufentanil for patient-controlled intravenous analgesia on the early recovery in elderly patients undergoing laparoscopic radical resection of rectal cancer].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 26;101(39):3238-3243. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20210504-01053. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34689537 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Buccal Acupuncture Reduces the Dose of Sufentanil Needed in Laparoscopic Gynecological Surgery.Med Sci Monit. 2025 Apr 23;31:e947088. doi: 10.12659/MSM.947088. Med Sci Monit. 2025. PMID: 40263917 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy of dexmedetomidine preemptive analgesia in breast tumor resection.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Dec 15;16(12):7343-7353. doi: 10.62347/HLKF8121. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39822527 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A, Cancer Statistics. 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(1):7–33. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

