IL-22RA2 Is a SMAD7 Target Mediating the Alleviation of Dermatitis and Psoriatic Phenotypes in Mice
- PMID: 37211203
- PMCID: PMC11127768
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jid.2023.04.029
IL-22RA2 Is a SMAD7 Target Mediating the Alleviation of Dermatitis and Psoriatic Phenotypes in Mice
Abstract
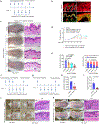
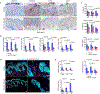
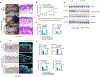
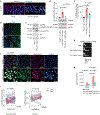
Long-term management of inflammatory skin diseases is challenging because of side effects from repeated use of systemic treatments or topical corticosteroids. This study sought to identify the mechanisms and developmental therapeutics for these diseases using genetic models and pharmacological approaches. We found that mice overexpressing SMAD7 in keratinocytes but not mice overexpressing the N-terminal domain of SMAD7 (i.e., N-SMAD7) were resistant to imiquimod-induced T helper 1/17- and T helper 2-type inflammation. We generated a Tat-PYC-SMAD7 (truncated SMAD7 protein encompassing C-terminal SMAD7 and PY motif fused with cell-penetrating Tat peptide). Topically applied Tat-PYC-SMAD7 to inflamed skin entered cells upon contact and attenuated imiquimod-, 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene-, and tape-stripping-induced inflammation. RNA-sequencing analyses of mouse skin exposed to these insults showed that in addition to inhibiting TGFβ/NF-κB, SMAD7 blunted IL-22/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 activation and associated pathogenesis, which is due to SMAD7 transcriptionally upregulating IL-22 antagonist IL-22RA2. Mechanistically, SMAD7 facilitated nuclear translocation and DNA binding of C/EBPβ to IL22RA2 promoter for IL22RA2 transactivation. Consistent with the observations in mice mentioned earlier, transcript levels of IL22RA2 were increased in human atopic dermatitis and psoriasis lesions with clinical remission. Our study identified the anti-inflammation functional domain of SMAD7 and suggests the mechanism and feasibility for developing SMAD7-based biologics as a topical therapy for skin inflammatory disorders.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
XJW and CDY are inventors of the patent filed by the University of Colorado for using SMAD7-based biologics as therapeutic agents. XJW is the founder of Allander Biotechnologies, which developed Tat-PYC-SMAD7. Allander Biotechnologies has an exclusive license from the University of Colorado in developing SMAD7-based therapy. The remaining authors state no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selenium-Rich Yeast Peptide Fraction Ameliorates Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Dermatitis in Mice by Inhibiting Inflammation via MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 14;23(4):2112. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042112. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216231 Free PMC article.
-
Khasianine ameliorates psoriasis-like skin inflammation and represses TNF-α/NF-κB axis mediated transactivation of IL-17A and IL-33 in keratinocytes.J Ethnopharmacol. 2022 Jun 28;292:115124. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115124. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35183690
-
Allicin ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation via disturbing the interaction of keratinocytes with IL-17A.Br J Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;180(5):628-646. doi: 10.1111/bph.15983. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Br J Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36355777
-
3, 3'- diindolylmethane hinders IL-17A/IL-17RA interaction and mitigates imiquimod-induced psoriasiform in mice.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Aug;109:108795. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108795. Epub 2022 Apr 26. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35487087
-
Smad7 Ameliorates TGF-β-Mediated Skin Inflammation and Associated Wound Healing Defects but Not Susceptibility to Experimental Skin Carcinogenesis.J Invest Dermatol. 2019 Apr;139(4):940-950. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.10.031. Epub 2018 Nov 10. J Invest Dermatol. 2019. PMID: 30423327 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cytotoxic and Immunomodulatory Effects of Hypericin as a Photosensitizer in Photodynamic Therapy Used on Skin Cell Cultures.Pharmaceutics. 2024 May 23;16(6):696. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16060696. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38931819 Free PMC article.
-
DUSP6 deletion protects mice and reduces disease severity in autoimmune arthritis.iScience. 2024 May 31;27(6):110158. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.110158. eCollection 2024 Jun 21. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38974475 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfei F, Kanev K, Hofmann M, Wu M, Ghoneim HE, Roelli P, et al. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection. Nature 2019;571:265–9. - PubMed
-
- Aranez V, Ambrus J Jr. Immunologic adverse effects of biologics for the treatment of atopy. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 2020;59:220–30. - PubMed
-
- Beck LA, Thaçi D, Hamilton JD, Graham NM, Bieber T, Rocklin R, et al. Dupilumab treatment in adults with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis. N Engl J Med 2014;371:130–9. - PubMed
-
- Bissonnette R, Pavel AB, Diaz A, Werth JL, Zang C, Vranic I, et al. Crisaborole and atopic dermatitis skin biomarkers: an intrapatient randomized trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2019;144:1274–89. - PubMed
-
- Boniface K, Bernard FX, Garcia M, Gurney AL, Lecron JC, Morel F. IL-22 inhibits epidermal differentiation and induces proinflammatory gene expression and migration of human keratinocytes. J Immunol 2005;174:3695–702. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

