Application of single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of novel breast cancer phenotypes based on the activation of ferroptosis-related genes
- PMID: 37212877
- PMCID: PMC10203036
- DOI: 10.1007/s10142-023-01086-0
Application of single-cell RNA sequencing analysis of novel breast cancer phenotypes based on the activation of ferroptosis-related genes
Abstract
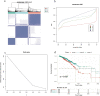
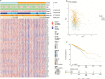
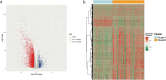
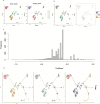
Ferroptosis is distinct from classic apoptotic cell death characterized by the accumulation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and lipid peroxides on the cell membrane. Increasing findings have demonstrated that ferroptosis plays an important role in cancer development, but the exploration of ferroptosis in breast cancer is limited. In our study, we aimed to establish a ferroptosis activation-related model based on the differentially expressed genes between a group exhibiting high ferroptosis activation and a group exhibiting low ferroptosis activation. By using machine learning to establish the model, we verified the accuracy and efficiency of our model in The Cancer Genome Atlas Breast Invasive Carcinoma (TCGA-BRCA) set and gene expression omnibus (GEO) dataset. Additionally, our research innovatively utilized single-cell RNA sequencing data to systematically reveal the microenvironment in the high and low FeAS groups, which demonstrated differences between the two groups from comprehensive aspects, including the activation condition of transcription factors, cell pseudotime features, cell communication, immune infiltration, chemotherapy efficiency, and potential drug resistance. In conclusion, different ferroptosis activation levels play a vital role in influencing the outcome of breast cancer patients and altering the tumor microenvironment in different molecular aspects. By analyzing differences in ferroptosis activation levels, our risk model is characterized by a good prognostic capacity in assessing the outcome of breast cancer patients, and the risk score can be used to prompt clinical treatment to prevent potential drug resistance. By identifying the different tumor microenvironment landscapes between the high- and low-risk groups, our risk model provides molecular insight into ferroptosis in breast cancer patients.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Ferroptosis; Single-cell RNA sequencing; Tumor microenvironment.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures









Similar articles
-
Predicting prognosis and clinical features of the tumor microenvironment based on ferroptosis score in patients with breast cancer.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 23;12(1):10611. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-14964-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35739315 Free PMC article.
-
Single-Cell RNA-Seq Analysis Reveals Ferroptosis in the Tumor Microenvironment of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 22;24(10):9092. doi: 10.3390/ijms24109092. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240436 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a ferroptosis-related prognostic model for the prediction of progression-free survival and immune microenvironment in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt A):108156. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108156. Epub 2021 Oct 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34624650
-
Ferroptosis-mediated immune responses in cancer.Front Immunol. 2023 May 30;14:1188365. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1188365. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37325669 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ferroptosis and its current progress in gastric cancer.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Feb 28;12:1289335. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1289335. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38481532 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ferroptosis and non-coding RNAs in breast cancer: insights into CAF and TAM interactions.Discov Oncol. 2025 Aug 31;16(1):1658. doi: 10.1007/s12672-025-03507-x. Discov Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40887542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YY1 regulates the proliferation and invasion of triple-negative breast cancer via activating PLAUR.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Aug 8;23(3):269. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-01193-y. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37552345
-
Targeting the initiator to activate both ferroptosis and cuproptosis for breast cancer treatment: progress and possibility for clinical application.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Jan 10;15:1493188. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1493188. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39867656 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

