SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR Ct values in saliva and nasopharyngeal swab samples for disease severity prediction
- PMID: 37213664
- PMCID: PMC10193917
- DOI: 10.1080/20002297.2023.2213106
SARS-CoV-2 RT-qPCR Ct values in saliva and nasopharyngeal swab samples for disease severity prediction
Abstract
Background: Comparison of clinical value of RT-qPCR-based SARS-CoV-2 tests performed on saliva samples (SSs) and nasopharyngeal swab samples (NPSs) for prediction of the COVID-19 disease severity.
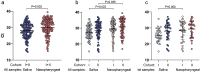
Methods: Three paired SSs and NPSs collected every 3 days from 100 hospitalised COVID-19 patients during 2020 Jul-2021 Jan were tested by RT-qPCR for the original SARS-CoV-2 virus and compared to 150 healthy controls. Cases were divided into mild+moderate (Cohort I, N = 47) and severe disease (Cohort II, N = 53) cohorts and compared.
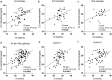
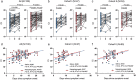
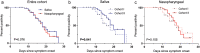
Results: SARS-CoV-2 was detected in 65% (91/140) vs. 53% (82/156) of NPSs and 49% (68/139) vs. 48% (75/157) of SSs collected from Cohort I and II, respectively, resulting in the total respective detection rates of 58% (173/296) vs. 48% (143/296) (P = 0.017). Ct values of SSs were lower than those of NPSs (mean Ct = 28.01 vs. 30.07, P = 0.002). Although Ct values of the first SSs were significantly lower in Cohort I than in Cohort II (P = 0.04), it became negative earlier (mean 11.7 vs. 14.8 days, P = 0.005). Multivariate Cox proportional hazards regression analysis showed that Ct value ≤30 from SSs was the independent predictor for severe COVID-19 (HR = 10.06, 95% CI: 1.84-55.14, P = 0.008).
Conclusion: Salivary RT-qPCR testing is suitable for SARS-CoV-2 infection control, while simple measurement of Ct values can assist in prediction of COVID-19 severity.
Keywords: COVID-19; Ct values; RT-qPCR; SARS-CoV-2; saliva; severity; viral dynamics.
© 2023 The Author(s). Published by Informa UK Limited, trading as Taylor & Francis Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Mantvydas Lopeta and Julius Gagilas are employees at JSC Diagnolita. JSC Diagnolita has developed the kits used in this research. The authors declare no other conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19 - 6 Apr 2023 [Internet]. [updated 2023 Apr 7]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on...
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
