Blood Pressure Reducing Potential and Renoprotective Action of Cilnidipine Among Hypertensive Patients Suffering From Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 37213948
- PMCID: PMC10194430
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.37774
Blood Pressure Reducing Potential and Renoprotective Action of Cilnidipine Among Hypertensive Patients Suffering From Chronic Kidney Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
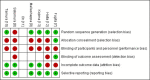
Hypertension is a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases which also causes progressive kidney damage leading to chronic kidney disease (CKD), so the rate of progression of CKD can be controlled by reducing blood pressure (BP). Many anti-hypertensive drugs are available. Cilnidipine is a new-generation calcium channel blocker (CCB). This meta-analysis is aimed to generate pooled evidence about the effectiveness of cilnidipine as an anti-hypertensive and to explore its reno-protective actions. Pubmed, Scopus, Cochrane Library, and Google Scholar were searched from January 2000 to December 2022 to include the studies. The pooled mean difference, along with 95% CI, was computed using Revman 5.4.1 software (Revman International, Inc., New York City, New York). The Cochrane risk-of-bias assessment tool was used for bias assessment. This meta-analysis was registered in PROSPERO with Reg. no. CRD42023395224. This meta-analysis included seven studies with 289 participants in the intervention group and 269 in the comparator group, and were selected from Japan, India, and Korea. Systolic blood pressure (SBP) was significantly reduced in cilnidipine treated group among hypertensives with CKD subjects weighted mean difference (WMD) was 4.33, and the 95% confidence interval (CI) was 1.26 to 7.31 as compared to the other group. Cilnidipine also shows a significant reduction in proteinuria with WMD 0.61 and 95% CI 0.42 to 0.80. Both groups were similar in adverse drug reactions (ADR). Cilnidipine is a more effective anti-hypertensive as compared to Amlodipine or other CCBs, mainly in reducing SBP. Besides this, cilnidipine also shows better reno-protective action because it also significantly reduces proteinuria in such patients.
Keywords: blood pressure; chronic kidney disease; cilnidipine; hypertension; proteinuria.
Copyright © 2023, Kumari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



References
-
- Wakar SS, Bonventre JV. Harrison's Principle of Internal Medicine. McGraw-Hill; 2022. Acute Kidney Injury.
-
- Hypertension in CKD: core curriculum 2019. Ku E, Lee BJ, Wei J, Weir MR. Am J Kidney Dis. 2019;74:120–131. - PubMed
-
- Nighttime hypertension in chronic kidney disease-are we in the dark without ambulatory blood pressure monitoring? Mayeda L, Rivara MB. JAMA Netw Open. 2022;5:0. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
