Are Two- and Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Scan Measurements of Tibial Tubercle-Trochlear Groove Distance Equivalent? A Comparative Study
- PMID: 37214363
- PMCID: PMC10192495
- DOI: 10.1007/s43465-023-00874-x
Are Two- and Three-Dimensional Computed Tomographic Scan Measurements of Tibial Tubercle-Trochlear Groove Distance Equivalent? A Comparative Study
Abstract
Background: Accurate planning for patellar instability correction is important in obtaining good post-operative outcome. The main challenge in the current two-dimensional (2-D) computed tomographic (CT) scans method is the difficulty in choosing reliable bony landmarks. This study aimed to compare the reliabilities between the 2-D and three-dimensional (3-D) methods of measuring tibial tubercle-trochlear groove (TT-TG) distance. We hypothesize that the proposed 3-D method will result in measurements with narrower error margin, providing higher reliability and accuracy.
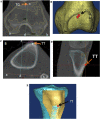
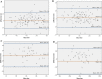
Materials and methods: We traced CT scans of 106 knees with no patellofemoral pathology from 59 subjects from the database system and converted all 2-D images into 3-D models to determine the values for each parameter. We compared the intra- and interobserver reliability of each method using intraclass correlation (ICC) and Bland-Altman method.
Results: The values of TT-TG measured by 2-D and 3-D methods were 16.1 ± 4.6 mm and 16.2 ± 4.2 mm, respectively. The ICC values of both methods were comparable (95% limits of agreement between the same observer: - 3.3 to 3.8 mm versus - 2.4 to 2.7 mm and different observers: - 4.3 to 4.9 mm versus - 3.9 to 2.7 mm), with 3-D method results in narrower limits of agreement.
Conclusion: TT-TG measurement is reliable using the 2-D method without using advanced radiographic software. The 3-D method of measuring TT-TG provides measurement with narrower variation when compared with the 2-D method. However, both TT-TG distances' measurement methods in the current study were comparable as the variations are not significant.
Keywords: CT scan; Inter- and intraobserver reliability; Intraclass correlation; Patellar instability; Three-dimensional model.
© Indian Orthopaedics Association 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of InterestAll authors declare that there are no conflicting interests.
Figures


References
-
- Carney JR, Mologne TS, Muldoon M, Cox JS. Long-term evaluation of the Roux-Elmslie-Trillat procedure for patellar instability. American Journal of Knee Surgery. 2005;33:1220–1223. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
