This is a preprint.
Disease-Modifying Effects of a Glial-targeted Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor (1400W) in Mixed-sex Cohorts of a Rat Soman (GD) Model of Epilepsy
- PMID: 37214912
- PMCID: PMC10197763
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2883247/v1
Disease-Modifying Effects of a Glial-targeted Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor (1400W) in Mixed-sex Cohorts of a Rat Soman (GD) Model of Epilepsy
Update in
-
Disease-modifying effects of a glial-targeted inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (1400W) in mixed-sex cohorts of a rat soman (GD) model of epilepsy.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jul 12;20(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02847-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37438764 Free PMC article.
Abstract
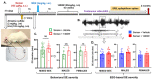
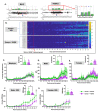
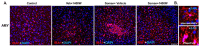
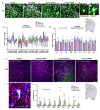
Background Acute exposure to seizurogenic organophosphate (OP) nerve agents (OPNA) such as diisopropylfluorophosphate (DFP) or soman (GD), at high concentrations, induce immediate status epilepticus (SE), reactive gliosis, neurodegeneration, and epileptogenesis as a consequence. Medical countermeasures (MCMs- atropine, oximes, benzodiazepines), if administered in < 20 minutes of OPNA exposure, can control acute symptoms and mortality. However, MCMs alone are inadequate to prevent OPNA-induced brain injury and behavioral dysfunction in survivors. We have previously shown that OPNA exposure-induced SE increases the production of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in glial cells in both short- and long- terms. Treating with a water soluble and highly selective iNOS inhibitor, 1400W, for three days significantly reduced OPNA-induced brain changes in those animals that had mild-moderate SE in the rat DFP model. However, such mitigating effects and the mechanisms of 1400W are unknown in a highly volatile nerve agent GD exposure. Methods Mixed-sex cohort of adult Sprague Dawley rats were exposed to GD (132µg/kg, s.c.) and immediately treated with atropine (2mg/kg, i.m) and HI-6 (125mg/kg, i.m.). Severity of seizures were quantified for an hour and treated with midazolam (3mg/kg, i.m.). An hour post-midazolam, 1400W (20mg/kg, i.m.) or vehicle was administered daily for two weeks. After behavioral testing and EEG acquisition, animals were euthanized at 3.5 months post-GD. Brains were processed for neuroinflammatory and neurodegeneration markers. Serum and CSF were used for nitrooxidative and proinflammatory cytokines assays. Results We demonstrate a significant long-term (3.5 months post-soman) disease-modifying effect of 1400W in animals that had severe SE for > 20min of continuous convulsive seizures. 1400W significantly reduced GD-induced motor and cognitive dysfunction; nitrooxidative stress (nitrite, ROS; increased GSH: GSSG); proinflammatory cytokines in the serum and some in the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); epileptiform spikes and spontaneously recurring seizures (SRS) in males; reactive gliosis (GFAP + C3 and IBA1 + CD68 positive glia) as a measure of neuroinflammation, and neurodegeneration (including parvalbumin positive neurons) in some brain regions. Conclusion These findings demonstrate the long-term disease-modifying effects of a glial-targeted iNOS inhibitor, 1400W, in a rat GD model by modulating reactive gliosis, neurodegeneration, and neuronal hyperexcitability.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
None
Figures





Similar articles
-
Disease-modifying effects of a glial-targeted inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitor (1400W) in mixed-sex cohorts of a rat soman (GD) model of epilepsy.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jul 12;20(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02847-1. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 37438764 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating organophosphate nerve agent, soman (GD), induced long-term neurotoxicity: Saracatinib, a Src Tyrosine Kinase inhibitor, as a potential countermeasure.J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Aug 5;22(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03520-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2025. PMID: 40764938 Free PMC article.
-
Mitigating Organophosphate Nerve Agent, Soman (GD)-Induced Long-Term Neurotoxicity: Saracatinib, a Src Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor, as a Potential Countermeasure.Res Sq [Preprint]. 2025 Jun 24:rs.3.rs-6674766. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-6674766/v1. Res Sq. 2025. Update in: J Neuroinflammation. 2025 Aug 5;22(1):199. doi: 10.1186/s12974-025-03520-5. PMID: 40678225 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Persistent behavior deficits, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in a rat model of acute organophosphate intoxication.Neurobiol Dis. 2020 Jan;133:104431. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.03.019. Epub 2019 Mar 21. Neurobiol Dis. 2020. PMID: 30905768 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exposure to nerve agents: from status epilepticus to neuroinflammation, brain damage, neurogenesis and epilepsy.Neurotoxicology. 2012 Dec;33(6):1476-1490. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2012.09.001. Epub 2012 Sep 7. Neurotoxicology. 2012. PMID: 23000013 Review.
References
-
- Gage M, Rao NS, Samidurai M, Putra M, Vasanthi SS, Meyer C, Wang C, Thippeswamy T (2022) Soman (GD) Rat Model to Mimic Civilian Exposure to Nerve Agent: Mortality, Video-EEG Based Status Epilepticus Severity, Sex Differences, Spontaneously Recurring Seizures, and Brain Pathology. Front Cell Neurosci. 10.3389/fncel.2021.798247 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hulse EJ, Haslam JD, Emmett SR, Woolley T (2019) Organophosphorus nerve agent poisoning: managing the poisoned patient. Br J Anaesth 123:457–463 - PubMed
-
- Nallapaneni A, Liu J, Karanth S, Pope C (2006) Modulation of paraoxon toxicity by the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2. Toxicology 227:173–183 - PubMed
-
- Jackson C, Ardinger C, Winter KM, McDonough JH, McCarren HS (2019) Validating a model of benzodiazepine refractory nerve agent-induced status epilepticus by evaluating the anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects of scopolamine, memantine, and phenobarbital. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 97:1–12 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

