This is a preprint.
Bile acid fitness determinants of a Bacteroides fragilis isolate from a human pouchitis patient
- PMID: 37214927
- PMCID: PMC10197588
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.11.540287
Bile acid fitness determinants of a Bacteroides fragilis isolate from a human pouchitis patient
Update in
-
Bile acid fitness determinants of a Bacteroides fragilis isolate from a human pouchitis patient.mBio. 2024 Jan 16;15(1):e0283023. doi: 10.1128/mbio.02830-23. Epub 2023 Dec 8. mBio. 2024. PMID: 38063424 Free PMC article.
Abstract
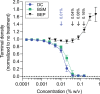
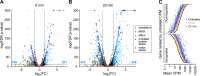
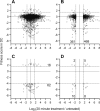
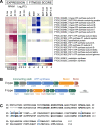
Bacteroides fragilis comprises 1-5% of the gut microbiota in healthy humans but can expand to >50% of the population in ulcerative colitis (UC) patients experiencing inflammation. The mechanisms underlying such microbial blooms are poorly understood, but the gut of UC patients has physicochemical features that differ from healthy patients and likely impact microbial physiology. For example, levels of the secondary bile acid deoxycholate (DC) are highly reduced in the ileoanal J-pouch of UC colectomy patients. We isolated a B. fragilis strain from a UC patient with pouch inflammation (i.e. pouchitis) and developed it as a genetic model system to identify genes and pathways that are regulated by DC and that impact B. fragilis fitness in DC and crude bile. Treatment of B. fragilis with a physiologically relevant concentration of DC reduced cell growth and remodeled transcription of one-quarter of the genome. DC strongly induced expression of chaperones and select transcriptional regulators and efflux systems and downregulated protein synthesis genes. Using a barcoded collection of ≈50,000 unique insertional mutants, we further defined B. fragilis genes that contribute to fitness in media containing DC or crude bile. Genes impacting cell envelope functions including cardiolipin synthesis, cell surface glycosylation, and systems implicated in sodium-dependent bioenergetics were major bile acid fitness factors. As expected, there was limited overlap between transcriptionally regulated genes and genes that impacted fitness in bile when disrupted. Our study provides a genome-scale view of a B. fragilis bile response and genetic determinants of its fitness in DC and crude bile.
Figures


References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
