This is a preprint.
Evidence of Bisphosphonate-Conjugated Sitafloxacin Eradication of Established Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus Infection with Osseointegration in Murine Models of Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis
- PMID: 37214929
- PMCID: PMC10197753
- DOI: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-2856287/v1
Evidence of Bisphosphonate-Conjugated Sitafloxacin Eradication of Established Methicillin-Resistant S. aureus Infection with Osseointegration in Murine Models of Implant-Associated Osteomyelitis
Update in
-
Evidence of bisphosphonate-conjugated sitafloxacin eradication of established methicillin-resistant S. aureus infection with osseointegration in murine models of implant-associated osteomyelitis.Bone Res. 2023 Oct 18;11(1):51. doi: 10.1038/s41413-023-00287-4. Bone Res. 2023. PMID: 37848449 Free PMC article.
Abstract
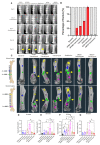
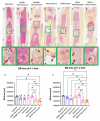
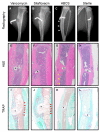
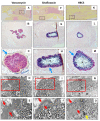
Eradication of MRSA osteomyelitis requires elimination of distinct biofilms. To overcome this, we developed bisphosphonate-conjugated sitafloxacin (BCS, BV600072) and hydroxybisphosphonate-conjugate sitafloxacin (HBCS, BV63072), which achieve "target-and-release" drug delivery proximal to the bone infection and have prophylactic efficacy against MRSA static biofilm in vitro and in vivo. Here we evaluated their therapeutic efficacy in a murine 1-stage exchange femoral plate model with bioluminescent MRSA (USA300LAC::lux). Osteomyelitis was confirmed by CFU on the explants and longitudinal bioluminescent imaging (BLI) after debridement and implant exchange surgery on day 7, and mice were randomized into seven groups: 1) Baseline (harvested at day 7, no treatment); 2) HPBP (bisphosphonate control for BCS) + vancomycin; 3) HPHBP (bisphosphonate control for HBCS) + vancomycin; 4) vancomycin; 5) sitafloxacin; 6) BCS + vancomycin; and 7) HBCS + vancomycin. BLI confirmed infection persisted in all groups except for mice treated with BCS or HBCS + vancomycin. Radiology revealed catastrophic femur fractures in all groups except mice treated with BCS or HBCS + vancomycin, which also displayed decreases in peri-implant bone loss, osteoclast numbers, and biofilm. To confirm this, we assessed the efficacy of vancomycin, sitafloxacin, and HBCS monotherapy in a transtibial implant model. The results showed complete lack of vancomycin efficacy, while all mice treated with HBCS had evidence of infection control, and some had evidence of osseous integrated septic implants, suggestive of biofilm eradication. Taken together these studies demonstrate that HBCS adjuvant with standard of care debridement and vancomycin therapy has the potential to eradicate MRSA osteomyelitis.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic; bisphosphonate; osteomyelitis; transmission electron microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: SS and FHE hold equity in BioVinc, LLC (Pasadena, CA) which sponsored this research. PC, SS, and FHE are inventors of patents related to this work.
Figures






References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

