This is a preprint.
Mild/Asymptomatic Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection Leads to Immune Paralysis in Fetal Circulation and Immune Dysregulation in Fetal-Placental Tissues
- PMID: 37214938
- PMCID: PMC10197637
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.05.10.540233
Mild/Asymptomatic Maternal SARS-CoV-2 Infection Leads to Immune Paralysis in Fetal Circulation and Immune Dysregulation in Fetal-Placental Tissues
Abstract
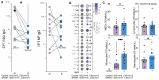
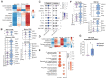
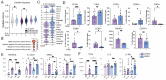
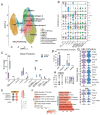
Few studies have addressed the impact of maternal mild/asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection on the developing neonatal immune system. In this study, we analyzed umbilical cord blood and placental chorionic villi from newborns of unvaccinated mothers with mild/asymptomatic SARSCoV-2 infection during pregnancy using flow cytometry, single-cell transcriptomics, and functional assays. Despite the lack of vertical transmission, levels of inflammatory mediators were altered in cord blood. Maternal infection was also associated with increased memory T, B cells, and non-classical monocytes as well as increased activation. However, ex vivo responses to stimulation were attenuated. Finally, within the placental villi, we report an expansion of fetal Hofbauer cells and infiltrating maternal macrophages and rewiring towards a heightened inflammatory state. In contrast to cord blood monocytes, placental myeloid cells were primed for heightened antiviral responses. Taken together, this study highlights dysregulated fetal immune cell responses in response to mild maternal SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy.
Keywords: COVID-19; Hofbauer cells; SARS-CoV-2; chorionic villi; placenta; umbilical cord blood.
Conflict of interest statement
COMPETING INTERESTS The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mild/asymptomatic COVID-19 in unvaccinated pregnant mothers impairs neonatal immune responses.JCI Insight. 2023 Sep 12;8(19):e172658. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.172658. JCI Insight. 2023. PMID: 37698937 Free PMC article.
-
Inefficient Placental Virus Replication and Absence of Neonatal Cell-Specific Immunity Upon Sars-CoV-2 Infection During Pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 3;12:698578. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.698578. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34149740 Free PMC article.
-
Hofbauer Cells Spread Listeria monocytogenes among Placental Cells and Undergo Pro-Inflammatory Reprogramming while Retaining Production of Tolerogenic Factors.mBio. 2021 Aug 31;12(4):e0184921. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01849-21. Epub 2021 Aug 17. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34399615 Free PMC article.
-
Placental SARS-CoV-2 in a pregnant woman with mild COVID-19 disease.J Med Virol. 2021 Feb;93(2):1038-1044. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26386. Epub 2020 Nov 10. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32749712 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hofbauer Cells: Placental Macrophages of Fetal Origin.Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017;62:45-60. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-54090-0_3. Results Probl Cell Differ. 2017. PMID: 28455705 Review.
References
-
- CDC. Data on COVID-19 during Pregnancy 2022. Available from: https://covid.cdc.gov/covid-data-tracker/#pregnant-population.
-
- Doyle TJ, Kiros GE, Schmitt-Matzen EN, Propper R, Thompson A, Phillips-Bell GS. Maternal and perinatal outcomes associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy, Florida, 2020–2021: A retrospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. Epub 20220608. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac441. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pulinx B, Kieffer D, Michiels I, Petermans S, Strybol D, Delvaux S, Baldewijns M, Raymaekers M, Cartuyvels R, Maurissen W. Vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection and preterm birth. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases. 2020;39(12):2441–5. doi: 10.1007/s10096-020-03964-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
