Exogenous Interleukin-37 Alleviates Hepatitis with Reduced Dendritic Cells and Induced Regulatory T Cells in Acute Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection
- PMID: 37215069
- PMCID: PMC10198762
- DOI: 10.1155/2023/1462048
Exogenous Interleukin-37 Alleviates Hepatitis with Reduced Dendritic Cells and Induced Regulatory T Cells in Acute Murine Cytomegalovirus Infection
Abstract
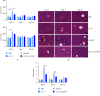
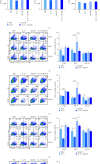
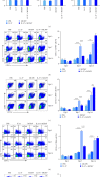
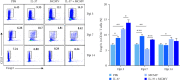
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection is globally distributed, and the liver is one of the major targeting organs. So far, the mechanisms for cell and organ damage have not fully been elucidated and the treatments for the infection are mainly at symptoms. IL-37 has shown a protective role in certain inflammatory diseases. In the present study, potential protective effect of exogenous IL-37 on murine cytomegalovirus- (MCMV-) infected hepatitis was evaluated through analyses of serum transaminases, the liver histopathology and cytokine expression, and functional state of dendritic cells (DCs) and regulatory T cells (Tregs). These analyses showed a significant decrease in serum transaminase levels and a lower Ishak histopathologic score at the early stage of MCMV-infected mice with exogenous IL-37 pretreatment. The frequencies of MHC-Ⅱ, CD40, CD80, and CD86 positive DCs in the liver and spleen were decreased significantly at 7 days postinfection (dpi) in MCMV-infected mice with IL-37 pretreatment when compared with those without the pretreatment, while the total number of DCs in the liver was reduced in IL-37-pretreated mice. The induction of Tregs in the spleen was enhanced at dpi 3 with IL-37 pretreatment in MCMV-infected mice. The mRNA expression levels of cytokines in the liver were decreased significantly (IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, IL-4) or to some extent (TGF-β and TNF-α). The present study suggested that exogenous IL-37 can alleviate MCMV-infected hepatitis, likely through reduced DCs and induced Tregs with a weaker cytokine storm, demonstrating its potential value in clinical management for HCMV-infected hepatitis.
Copyright © 2023 Yufei Ruan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Role of Autophagy in Murine Cytomegalovirus Hepatitis.Viral Immunol. 2021 May;34(4):241-255. doi: 10.1089/vim.2020.0024. Epub 2021 Feb 9. Viral Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33566740
-
Expression pattern of CD11c on lung immune cells after disseminated murine cytomegalovirus infection.Virol J. 2017 Jul 18;14(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12985-017-0801-x. Virol J. 2017. PMID: 28720115 Free PMC article.
-
Regulatory T cells and T-cell-derived IL-10 interfere with effective anti-cytomegalovirus immune response.Immunol Cell Biol. 2014 Nov;92(10):860-71. doi: 10.1038/icb.2014.62. Epub 2014 Jul 29. Immunol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 25070242
-
The roles of tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1 and interleukin-12 in murine cytomegalovirus infection.Immunology. 1997 May;91(1):45-52. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2567.1997.00226.x. Immunology. 1997. PMID: 9203964 Free PMC article.
-
Murine cytomegalovirus retinitis during MAIDS: Susceptibility correlates with elevated intraocular levels of interleukin-4 mRNA.Curr Eye Res. 2003 Mar-Apr;26(3-4):211-7. doi: 10.1076/ceyr.26.3.211.14902. Curr Eye Res. 2003. PMID: 12815549
Cited by
-
IL-37 Mitigates the Inflammatory Response in Macrophages Induced by SARS-CoV-2 Omicron Infection Through the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.MedComm (2020). 2025 May 31;6(6):e70229. doi: 10.1002/mco2.70229. eCollection 2025 Jun. MedComm (2020). 2025. PMID: 40452816 Free PMC article.
-
Role of IL-1 Family Cytokines IL-36, IL-37, IL-38 in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Comprehensive Review.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jun 20;17:4001-4016. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S474879. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38915806 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

