Unorthodox localization of P2X7 receptor in subcellular compartments of skeletal system cells
- PMID: 37215083
- PMCID: PMC10192554
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1180774
Unorthodox localization of P2X7 receptor in subcellular compartments of skeletal system cells
Abstract
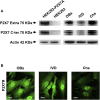
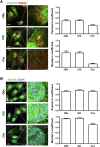
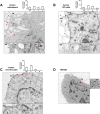
Identifying the subcellular localization of a protein within a cell is often an essential step in understanding its function. The main objective of this report was to determine the presence of the P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) in healthy human cells of skeletal system, specifically osteoblasts (OBs), chondrocytes (Chs) and intervertebral disc (IVD) cells. This receptor is a member of the ATP-gated ion channel family, known to be a main sensor of extracellular ATP, the prototype of the danger signal released at sites of tissue damage, and a ubiquitous player in inflammation and cancer, including bone and cartilaginous tissues. Despite overwhelming data supporting a role in immune cell responses and tumor growth and progression, a complete picture of the pathophysiological functions of P2X7R, especially when expressed by non-immune cells, is lacking. Here we show that human wild-type P2X7R (P2X7A) was expressed in different samples of human osteoblasts, chondrocytes and intervertebral disc cells. By fluorescence microscopy (LM) and immunogold transmission electron microscopy we localized P2X7R not only in the canonical sites (plasma membrane and cytoplasm), but also in the nucleus of all the 3 cell types, especially IVD cells and OBs. P2X7R mitochondrial immunoreactivity was predominantly detected in OBs and IVD cells, but not in Chs. Evidence of subcellular localization of P2X7R may help to i. understand the participation of P2X7R in as yet unidentified signaling pathways in the joint and bone microenvironment, ii. identify pathologies associated with P2X7R mislocalization and iii. design specific targeted therapies.
Keywords: P2X7 receptor; chondrocytes; immunogold and electron microscopy; intervertebral disc cells; osteoblasts; purinergic signaling; subcellular localization.
Copyright © 2023 Penolazzi, Notarangelo, Lambertini, Vultaggio-Poma, Tarantini, Di Virgilio and Piva.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Adinolfi E., Callegari M. G., Ferrari D., Bolognesi C., Minelli M., Wieckowski M. R., et al. (2005). Basal activation of the P2X7 ATP receptor elevates mitochondrial calcium and potential, increases cellular ATP levels, and promotes serum-independent growth. Mol. Biol. Cell 16 (7), 3260–3272. 10.1091/mbc.e04-11-1025 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

