Precision antiplatelet therapy
- PMID: 37215094
- PMCID: PMC10193296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.rpth.2023.100138
Precision antiplatelet therapy
Abstract
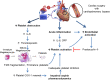
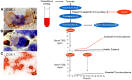
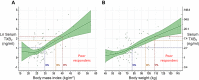
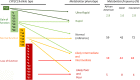
A State of the Art lecture titled "Personalizing Antiplatelet Therapy Based on Platelet Turnover and Metabolic Phenotype" was presented by Bianca Rocca at the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) Congress in 2022. Increased variability in drug response may be associated with serious, mechanism-based and off-target side effects, especially in the case of drugs that do not routinely undergo therapeutic drug monitoring, such as antiplatelet drugs or direct oral anticoagulants. Precision pharmacology can be defined as the identification of a drug regimen that maximizes the benefit/risk balance at the level of an individual patient. Key tools for identifying relevant sources of variability and developing precision drug dosing are represented by genetic, biochemical, and pharmacological biomarkers recognized as a valid surrogate or strong predictor of major clinical complications. Pharmacodynamic, pharmacokinetic, and/or disease-related biomarkers are central to identifying the right population to be targeted, characterizing the sources of variability in drug response, guiding precision treatments that maximize benefits and minimize risks, and designing precision dosing trials. Another valuable tool for guiding precision pharmacology is represented by in silico pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic models and simulations instructed by real-world data of validated biomarkers. This review critically analyzes the tools for precision dosing and exemplifies conditions in which precision dosing can considerably optimize the efficacy and safety of antiplatelet drugs, namely aspirin and P2Y12 receptor blockers, used alone and in combination. Finally, we summarize relevant new data on this topic presented during the 2022 ISTH Congress.
Keywords: arterial occlusive diseases; aspirin; platelet aggregation inhibitors; precision medicine; purinergic P2Y receptor antagonists.
© 2023 The Authors.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Advocating cardiovascular precision medicine with P2Y12 receptor inhibitors.Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2017 Oct 1;3(4):221-234. doi: 10.1093/ehjcvp/pvw044. Eur Heart J Cardiovasc Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28204303 Review.
-
Antiplatelet agents.Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009:267-72. doi: 10.1182/asheducation-2009.1.267. Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2009. PMID: 20008209 Review.
-
Clinical pharmacology of antiplatelet drugs.Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Oct;15(10):1177-1197. doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2121702. Epub 2022 Sep 11. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36065676 Review.
-
Antiplatelet drugs--do we need new options? With a reappraisal of direct thromboxane inhibitors.Drugs. 2010 May 7;70(7):887-908. doi: 10.2165/11536000-000000000-00000. Drugs. 2010. PMID: 20426498 Review.
-
Population pharmacodynamic modelling of aspirin- and Ibuprofen-induced inhibition of platelet aggregation in healthy subjects.Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008;47(2):129-37. doi: 10.2165/00003088-200847020-00006. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2008. PMID: 18193919 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Stability of the thromboxane B2 biomarker of low-dose aspirin pharmacodynamics in human whole blood and in long-term stored serum samples.Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024 Nov 12;8(8):102623. doi: 10.1016/j.rpth.2024.102623. eCollection 2024 Nov. Res Pract Thromb Haemost. 2024. PMID: 39698184 Free PMC article.
-
Oral P2Y12 Inhibitors: Victims or Perpetrators? A Focused Review on Pharmacokinetic, Clinically Relevant Drug Interactions.Eur Cardiol. 2025 Jun 11;20:e17. doi: 10.15420/ecr.2025.12. eCollection 2025. Eur Cardiol. 2025. PMID: 40556646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mullard A. Parsing clinical success rates. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:447. - PubMed
-
- Eichler H.G., Abadie E., Breckenridge A., Flamion B., Gustafsson L.L., Leufkens H., et al. Bridging the efficacy-effectiveness gap: a regulator's perspective on addressing variability of drug response. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:495–506. - PubMed
-
- Peck R.W., Shahin M.H., Vinks A.A. Precision dosing: the clinical pharmacology of Goldilocks. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 2021;109:11–14. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

