Single-swap editing for the correction of common Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations
- PMID: 37215149
- PMCID: PMC10192335
- DOI: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.04.009
Single-swap editing for the correction of common Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations
Abstract
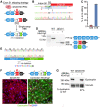
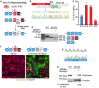
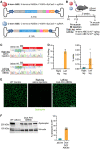
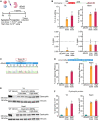
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is a fatal X-linked recessive disease of progressive muscle weakness and wasting caused by the absence of dystrophin protein. Current gene therapy approaches using antisense oligonucleotides require lifelong dosing and have limited efficacy in restoring dystrophin production. A gene editing approach could permanently correct the genome and restore dystrophin protein expression. Here, we describe single-swap editing, in which an adenine base editor edits a single base pair at a splice donor site or splice acceptor site to enable exon skipping or reframing. In human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes, we demonstrate that single-swap editing can enable beneficial exon skipping or reframing for the three most therapeutically relevant exons-DMD exons 45, 51, and 53-which could be beneficial for 30% of all DMD patients. Furthermore, an adeno-associated virus delivery method for base editing components can efficiently restore dystrophin production locally and systemically in skeletal and cardiac muscles of a DMD mouse model containing a deletion of Dmd exon 44. Our studies demonstrate single-swap editing as a potential gene editing therapy for common DMD mutations.
Keywords: AAV; CRISPR-Cas9; DMD; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; MT: RNA/DNA editing; base editing; exon skipping; gene editing; iPSC; iPSC-CM.
© 2023 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F.C., R.B.-D., and E.N.O. have filed patent applications related to this work. E.N.O. is a consultant for Vertex Pharmaceuticals and Tenaya Therapeutics.
Figures


References
-
- Birnkrant D.J., Bushby K., Bann C.M., Apkon S.D., Blackwell A., Brumbaugh D., Case L.E., Clemens P.R., Hadjiyannakis S., Pandya S., et al. DMD Care Considerations Working Group Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 1: diagnosis, and neuromuscular, rehabilitation, endocrine, and gastrointestinal and nutritional management. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:251–267. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30024-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Birnkrant D.J., Bushby K., Bann C.M., Alman B.A., Apkon S.D., Blackwell A., Case L.E., Cripe L., Hadjiyannakis S., Olson A.K., et al. DMD Care Considerations Working Group Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, part 2: respiratory, cardiac, bone health, and orthopaedic management. Lancet Neurol. 2018;17:347–361. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(18)30025-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bladen C.L., Salgado D., Monges S., Foncuberta M.E., Kekou K., Kosma K., Dawkins H., Lamont L., Roy A.J., Chamova T., et al. The TREAT-NMD DMD Global Database: analysis of more than 7,000 Duchenne muscular dystrophy mutations. Hum. Mutat. 2015;36:395–402. doi: 10.1002/humu.22758. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Min Y.L., Li H., Rodriguez-Caycedo C., Mireault A.A., Huang J., Shelton J.M., McAnally J.R., Amoasii L., Mammen P.P.A., Bassel-Duby R., Olson E.N. CRISPR-Cas9 corrects Duchenne muscular dystrophy exon 44 deletion mutations in mice and human cells. Sci. Adv. 2019;5:eaav4324. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aav4324. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

