Isothermal nucleic acid amplification and its uses in modern diagnostic technologies
- PMID: 37215369
- PMCID: PMC10193355
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-023-03628-6
Isothermal nucleic acid amplification and its uses in modern diagnostic technologies
Abstract
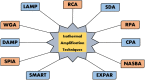
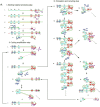
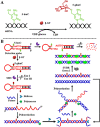
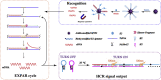
Nucleic acids are prominent biomarkers for diagnosing infectious pathogens using nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAATs). PCR, a gold standard technique for amplifying nucleic acids, is widely used in scientific research and diagnosis. Efficient pathogen detection is a key to adequate food safety and hygiene. However, using bulky thermal cyclers and costly laboratory setup limits its uses in developing countries, including India. The isothermal amplification methods are exploited to develop miniaturized sensors against viruses, bacteria, fungi and other pathogenic organisms and have been applied for in situ diagnosis. Isothermal amplification techniques have been found suitable for POC techniques and follow WHO's ASSURED criteria. LAMP, NASBA, SDA, RCA and RPA are some of the isothermal amplification techniques which are preferable for POC diagnostics. Furthermore, methods such as WGA, CPA, HDA, EXPAR, SMART, SPIA and DAMP were introduced for even more accuracy and robustness. Using recombinant polymerases and other nucleic acid-modifying enzymes has dramatically broadened the detection range of target pathogens under the scanner. The coupling of isothermal amplification methods with advanced technologies such as CRISPR/Cas systems, fluorescence-based chemistries, microfluidics and paper-based sensors has significantly influenced the biosensing and diagnosis field. This review comprehensively analyzed isothermal nucleic acid amplification methods, emphasizing their advantages, disadvantages and limitations.
Keywords: ASSURED; Isothermal DNA amplification; LAMP; Point of care device.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2023, Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Abirami N, Nidaullah H, Chuah LO, Shamila-Syuhada AK, Chandraprasad SR, Huda N, Hasmaizal H, Rusul G. Evaluation of commercial loop-mediated isothermal amplification-based kit and ready-to use plating system for detection of Salmonella in naturally contaminated poultry and their processing environment. Food Control. 2016;70:74–78. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.05.035. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

