Effectiveness of Ponseti technique in management of arthrogrypotic clubfeet - a prospective study
- PMID: 37215511
- PMCID: PMC10195217
Effectiveness of Ponseti technique in management of arthrogrypotic clubfeet - a prospective study
Abstract
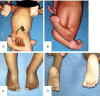
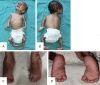
Background: Clubfoot constitutes roughly 70 percent of all foot deformities in arthrogryposis syndrome and 98% of those in classic arthrogryposis. Treatment of arthrogrypotic clubfoot is difficult and challenging due to a combination of factors like stiffness of ankle-foot complex, severe deformities and resistance to conventional treatment, frequent relapses and the challenge is further compounded by presence of associated hip and knee contractures.
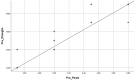
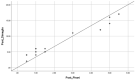
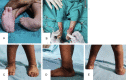
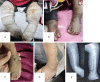
Method: A prospective clinical study was conducted using a sample of nineteen clubfeet in twelve arthrogrypotic children. During weekly visits Pirani and Dimeglio scores were assigned to each foot followed by manipulation and serial cast application according to the classical Ponseti technique. Mean initial Pirani score and Dimeglio score were 5.23 ± 0.5 and 15.79 ± 2.4 respectively. Mean Pirani and Dimeglio score at last follow up were 2.37 ± 1.9 and 8.26 ± 4.93 respectively. An average of 11.3 casts was required to achieve correction. Tendoachilles tenotomy was required in all 19 AMC clubfeet.
Result: The primary outcome measure was to evaluate the role of Ponseti technique in management of arthrogrypotic clubfeet. The secondary outcome measure was to study the possible causes of relapses and complications with additional procedures required to manage clubfeet in AMC an initial correction was achieved in 13 out of 19 arthrogrypotic clubfeet (68.4%). Relapse occurred in 8 out of 19 clubfeet. Five of those relapsed feet were corrected by re-casting ± tenotomy. 52.6% of arthrogrypotic clubfeet were successfully treated by the Ponseti technique in our study. Three patients failed to respond to Ponseti technique required some form of soft tissue surgery.
Conclusion: Based on our results, we recommend the Ponseti technique as the first line initial treatment for arthrogrypotic clubfeet. Although such feet require a higher number of plaster casts with a higher rate of tendo-achilles tenotomy but the eventual outcome is satisfactory. Although, relapses are higher than classical idiopathic clubfeet, most of them respond to re-manipulation and serial casting ± re-tenotomy.
Keywords: Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita (AMC); Dimeglio score; Pirani score; Ponseti technique; clubfeet; relapse; tenotomy.
IJBT Copyright © 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Outcomes of Ponseti Method for the Treatment of Clubfeet in Children With Arthrogryposis.J Pediatr Orthop. 2024 Sep 1;44(8):508-512. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0000000000002715. Epub 2024 Apr 30. J Pediatr Orthop. 2024. PMID: 38689454
-
Early results of the Ponseti method for the treatment of clubfoot in distal arthrogryposis.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008 Jul;90(7):1501-7. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.G.00563. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008. PMID: 18594099
-
Ponseti Casting and Achilles Release Versus Classic Casting and Soft Tissue Releases for the Initial Treatment of Arthrogrypotic Clubfeet.Foot Ankle Int. 2015 Sep;36(9):1072-7. doi: 10.1177/1071100715581656. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Foot Ankle Int. 2015. PMID: 25925945
-
Interventions for congenital talipes equinovarus (clubfoot).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 May 15;5(5):CD008602. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD008602.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32412098 Free PMC article.
-
The Ponseti method of treatment for neuromuscular and syndromic (non-idiopathic) clubfeet: evaluation of a programme-based approach at a mean follow-up of 5.8 years.Int Orthop. 2021 Jan;45(1):155-163. doi: 10.1007/s00264-020-04677-9. Epub 2020 Jul 10. Int Orthop. 2021. PMID: 32651710 Review.
Cited by
-
Midterm clinical and radiological outcomes of arthrogryposis-associated clubfoot treated with the Ponseti method: a retrospective observational study and comprehensive literature review.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Sep 28;19(1):595. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05101-3. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39342344 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lloyd-Roberts GC, Lettin AWF. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1970;52:494–508. - PubMed
-
- Boehm S, Limpaphayom N, Alaee F, Sinclair MF, Dobbs MB. Early results of the Ponseti method for the treatment of clubfoot in distal arthrogryposis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90:1501–7. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein RM. Arthrogryposis and amyoplasia. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2002;10:417–24. - PubMed
-
- Hall JG. Arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: etiology, genetics, classification, diagnostic approach, and general aspects. J Pediatr Orthop B. 1997;6:159–66. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
