Antiphospholipid antibodies induce proinflammatory and procoagulant pathways in endothelial cells
- PMID: 37216142
- PMCID: PMC10197110
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtauto.2023.100202
Antiphospholipid antibodies induce proinflammatory and procoagulant pathways in endothelial cells
Abstract
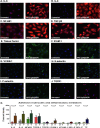
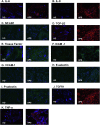
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune thrombophilia characterized by recurrent thrombotic events and/or pregnancy morbidity in the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies detected either as anti-cardiolipin, anti-β2 Glycoprotein I (anti-β2GPI) or Lupus anticoagulant (LA). Endothelial deregulation characterizes the syndrome. To address gene expression changes accompanying the development of autoimmune phenotype in endothelial cells in the context of APS, we performed transcriptomics analysis in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs) stimulated with IgG from APS patients and β2GPI, followed by intersection of RNA-seq data with published microarray and ChIP-seq results (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation). Our strategy revealed that during HUVEC activation diverse signaling pathways such as TNF-α, TGF-β, MAPK38, and Hippo are triggered as indicated by Gene Ontology (GO) classification and pathway analysis. Finally, cell biology approaches performed side-by-side in naïve and stimulated cultured HUVECs, as well as, in placenta specimens derived from Healthy donors (HDs) and APS-patients verified the evolution of an APS-characteristic gene expression program in endothelial cells during the initial stages of the disease's development.
Keywords: Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS); Computational biology tools; Gene expression programs; Inflammatory and procoagulant phenotype; Transcriptional regulators; Transcriptomics analysis.
© 2023 Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Professor Panayiotis G Vlachoyiannopoulos reports financial support was provided by 10.13039/501100003447State Scholarships Foundation.
Figures



References
-
- McNeil H.P., Chesterman C.N., Krilis S.A. Immunology and clinical importance of antiphospholipid antibodies. Adv. Immunol. 1991;49:193–280. - PubMed
-
- Bevers E.M., Galli M., Barbui T., Comfurius P., Zwaal R.F. Lupus anticoagulant IgG's (LA) are not directed to phospholipids only, but to a complex of lipid-bound human prothrombin. Thromb. Haemostasis. 1991;66(6):629–632. - PubMed
-
- Cervera R., Piette J.C., Font J., et al. Antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical and immunologic manifestations and patterns of disease expression in a cohort of 1,000 patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(4):1019–1027. - PubMed
-
- Mehdi A.A., Uthman I., Khamashta M. Antiphospholipid syndrome: pathogenesis and a window of treatment opportunities in the future. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2010;40(5):451–464. - PubMed
-
- Pierangeli S.S., Vega-Ostertag M.E., Gonzalez E.B. New targeted therapies for treatment of thrombosis in antiphospholipid syndrome. Expet Rev. Mol. Med. 2007;9(30):1–15. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

