Conventional heart failure therapy in cardiac ATTR amyloidosis
- PMID: 37216684
- PMCID: PMC10424879
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad347
Conventional heart failure therapy in cardiac ATTR amyloidosis
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Conventional heart failure therapy in cardiac ATTR amyloidosis.Eur Heart J. 2024 Apr 7;45(14):1251. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehae140. Eur Heart J. 2024. PMID: 38428942 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Aims: The aims of this study were to assess prescription patterns, dosages, discontinuation rates, and association with prognosis of conventional heart failure medications in patients with transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis (ATTR-CA).
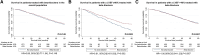
Methods and results: A retrospective analysis of all consecutive patients diagnosed with ATTR-CA at the National Amyloidosis Centre between 2000 and 2022 identified 2371 patients with ATTR-CA. Prescription of heart failure medications was greater among patients with a more severe cardiac phenotype, comprising beta-blockers in 55.4%, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEis)/angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) in 57.4%, and mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRAs) in 39.0% of cases. During a median follow-up of 27.8 months (interquartile range 10.6-51.3), 21.7% had beta-blockers discontinued, and 32.9% had ACEi/ARBs discontinued. In contrast, only 7.5% had MRAs discontinued. A propensity score-matched analysis demonstrated that treatment with MRAs was independently associated with a reduced risk of mortality in the overall population [hazard ratio (HR) 0.77 (95% confidence interval (CI) 0.66-0.89), P < .001] and in a pre-specified subgroup of patients with a left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) >40% [HR 0.75 (95% CI 0.63-0.90), P = .002]; and treatment with low-dose beta-blockers was independently associated with a reduced risk of mortality in a pre-specified subgroup of patients with a LVEF ≤40% [HR 0.61 (95% CI 0.45-0.83), P = .002]. No convincing differences were found for treatment with ACEi/ARBs.
Conclusion: Conventional heart failure medications are currently not widely prescribed in ATTR-CA, and those that received medication had more severe cardiac disease. Beta-blockers and ACEi/ARBs were often discontinued, but low-dose beta-blockers were associated with reduced risk of mortality in patients with a LVEF ≤40%. In contrast, MRAs were rarely discontinued and were associated with reduced risk of mortality in the overall population; but these findings require confirmation in prospective randomized controlled trials.
Keywords: Beta-blockers; Cardiac ATTR amyloidosis; Heart failure; Heart failure medications; Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures



Comment in
-
Neurohormonal blockade in transthyretin amyloidosis: perhaps one size does not fit all?Eur Heart J. 2023 Aug 14;44(31):2908-2910. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehad357. Eur Heart J. 2023. PMID: 37224517 No abstract available.

