Monkeypox viral nucleic acids detected using both DNA and RNA extraction workflows
- PMID: 37216988
- PMCID: PMC10213602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.164289
Monkeypox viral nucleic acids detected using both DNA and RNA extraction workflows
Abstract
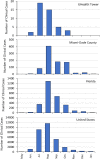
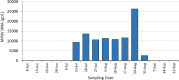
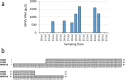
Molecular methods have been used to detect human pathogens in wastewater with sampling typically performed at wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) and upstream locations within the sewer system. A wastewater-based surveillance (WBS) program was established at the University of Miami (UM) in 2020, which included measurements of SARS-CoV-2 levels in wastewater from its hospital and within the regional WWTP. In addition to the development of a SARS-CoV-2 quantitative PCR (qPCR) assay, qPCR assays to detect other human pathogens of interest were also developed at UM. Here we report on the use of a modified set of reagents published by the CDC to detect nucleic acids of Monkeypox virus (MPXV) which emerged during May of 2022 to become a concern worldwide. Samples collected from the University hospital and from the regional WWTP were processed through DNA and RNA workflows and analyzed by qPCR to detect a segment of the MPXV CrmB gene. Results show positive detections of MPXV nucleic acids in the hospital and wastewater treatment plant wastewater which coincided with clinical cases in the community and mirrored the overall trend of nationwide MPXV cases reported to the CDC. We recommend the expansion of current WBS programs' methods to detect a broader range of pathogens of concern in wastewater and present evidence that viral RNA in human cells infected by a DNA virus can be detected in wastewater.
Keywords: COVID-19; MPXV; Monkeypox virus; Mpox; SARS-CoV-2 wastewater-based surveillance; Wastewater.
Copyright © 2023 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Aden T.A., Blevins P., York S.W., Rager S., Balachandran D., Hutson C.L., Lowe D., Mangal C.N., Wolford T., Matheny A., Davidson W., Wilkins K., Cook R., Roulo R.M., White M.K., Berman L., Murray J., Laurance J., Francis D., Green N.M., Berumen R.A., 3rd, Gonzalez A., Evans S., Hudziec M., Noel D., Adjei M., Hovan G., Lee P., Tate L., Gose R.B., Voermans R., Crew J., Adam P.R., Haydel D., Lukula S., Matluk N., Shah S., Featherston J., Ware D., Pettit D., McCutchen E., Acheampong E., Buttery E., Gorzalski A., Perry M., Fowler R., Lee R.B., Nickla R., Huard R., Moore A., Jones K., Johnson R., Swaney E., Jaramillo J., Reinoso Webb C., Guin B., Yost J., Atkinson A., Griffin-Thomas L., Chenette J., Gant J., Sterkel A., Ghuman H.K., Lute J., Smole S.C., Arora V., Demontigny C.K., Bielby M., Geeter E., Newman K.A.M., Glazier M., Lutkemeier W., Nelson M., Martinez R., Chaitram J., Honein M.A., Villanueva J.M. Rapid diagnostic testing for response to the monkeypox outbreak - Laboratory Response Network, United States, May 17–June 30, 2022. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly Rep. 2022;71(28):904–907. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atoui A., Jourdain F., Mouly D., Cordevant C., Chesnot T., Gassilloud B. A review on mpox (monkeypox) virus shedding in wastewater and its presistence evaluation in environmental samples. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2023:7.
-
- Baaijens J.A., Zuuli A., Ott I.M., Petrone M.E., Alpert T., Fauver J.R., Kalinich C.C., Vogels C.B.F., Breban M.I., Duvallet C., McElroy K., Ghaeli N., Imakaev M., Mckenzie-Bennett M., Robison K., Plocik A., Schilling R., Pierson M., Littlefield R., Spencer M., Simen B.B., Initiative Y.S.-C.-G.S., Hanage W.P., Grubaugh N.D., Peccia J., Baym M. Variant abundance estimation for SARS-CoV-2 in wastewater using RNA-Seq quantification. medRxiv. 2021 (preprint)
-
- Babler K.M., Amirali A., Sharkey M.E., Williams S.L., Boone M.M., Cosculluela G.A., Currall B.B., Grills G.S., Laine J., Mason C.E., Reding B.D., Schurer S.C., Stevenson M., Vidovic D., Solo-Gabriele H.M. Comparison of electronegative filtration to magnetic bead-based concentration and V2G-qPCR to RT-qPCR for quantifying viral SARS-CoV-2 RNA from wastewater. ACS ES T Water. 2022;2(11):2004–2013. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Babler K.M., Sharkey M.E., Abelson S., Amirali A., Benitez A., Cosculluela G.A., Grills G.S., Kumar N., Laine J., Lamar W., Lamm E.D., Lyu J., Mason C.E., McCabe P.M., Raghavender J., Reding B.D., Roca M.A., Schurer S.C., Stevenson M., Szeto A., Tallon J.J., Jr., Vidovic D., Zarnegarnia Y., Solo-Gabriele H.M. Degradation rates influence the ability of composite samples to represent 24-hourly means of SARS-CoV-2 and other microbiological target measures in wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2023;867 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

