Ideological values are parametrically associated with empathy neural response to vicarious suffering
- PMID: 37217192
- PMCID: PMC10281241
- DOI: 10.1093/scan/nsad029
Ideological values are parametrically associated with empathy neural response to vicarious suffering
Abstract
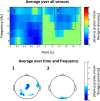
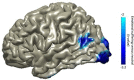
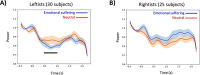
Several studies in political psychology reported higher levels of empathy among political leftists (i.e. liberals) as compared to political rightists (i.e. conservatives). Yet, all those studies lean on self-reports, which are often limited by subjective bias and conformity to social norms. Here, we tested this putative asymmetry using neuroimaging: we recorded oscillatory neural activity using magnetoencephalography while 55 participants completed a well-validated neuroimaging paradigm for empathy to vicarious suffering. The findings revealed a typical rhythmic alpha-band 'empathy response' in the temporal-parietal junction. This neural empathy response was significantly stronger in the leftist than in the rightist group. In addition to this dichotomous division, the neural response was parametrically associated with both self-reported political inclination and right-wing ideological values. This is the first study to reveal an asymmetry in the neural empathy response as a function of political ideology. The findings reported in this study are in line with the current literature in political psychology and provide a novel neural perspective to support the ideological asymmetry in empathy. This study opens new vistas for addressing questions in political psychology by using neuroimaging.
Keywords: alpha rhythm; empathy; ideological asymmetry; magnetoencephalography; neuropolitics.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they had no conflict of interest with respect to their authorship or the publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Alford J.R., Funk C.L., Hibbing J.R. (2005). Are political orientations genetically transmitted? American Political Science Review, 99(2), 153–67.
-
- Altemeyer B. (1983). Right-Wing Authoritarianism. Winnipeg, Manitoba: University of Manitoba Press.
-
- Amodio D.M., Jost J.T., Master S.L., et al. (2007). Neurocognitive correlates of liberalism and conservatism. Nature Neuroscience, 10(10), 1246–7. - PubMed
-
- Bäckström M., Björklund F. (2007). Structural modeling of generalized prejudice: the role of social dominance, authoritarianism, and empathy. Journal of Individual Differences, 28(1), 10–7.

