Whole genome sequencing and analysis of Armillaria gallica Jzi34 symbiotic with Gastrodia elata
- PMID: 37217849
- PMCID: PMC10204328
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09384-4
Whole genome sequencing and analysis of Armillaria gallica Jzi34 symbiotic with Gastrodia elata
Abstract
Background: Armillaria species are plant pathogens, but a few Armillaria species can establish a symbiotic relationship with Gastrodia elata, a rootless and leafless orchid, that is used as a Chinese herbal medicine. Armillaria is a nutrient source for the growth of G. elata. However, there are few reports on the molecular mechanism of symbiosis between Armillaria species and G. elata. The genome sequencing and analysis of Armillaria symbiotic with G. elata would provide genomic information for further studying the molecular mechanism of symbiosis.
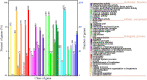
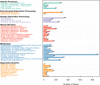
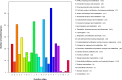
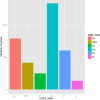
Results: The de novo genome assembly was performed with the PacBio Sequel platform and Illumina NovaSeq PE150 for the A. gallica Jzi34 strain, which was symbiotic with G. elata. Its genome assembly contained ~ 79.9 Mbp and consisted of 60 contigs with an N50 of 2,535,910 bp. There were only 4.1% repetitive sequences in the genome assembly. Functional annotation analysis revealed a total of 16,280 protein coding genes. Compared with the other five genomes of Armillaria, the carbohydrate enzyme gene family of the genome was significantly contracted, while it had the largest set of glycosyl transferase (GT) genes. It also had an expansion of auxiliary activity enzymes AA3-2 gene subfamily and cytochrome P450 genes. The synteny analysis result of P450 genes reveals that the evolutionary relationship of P450 proteins between A. gallica Jzi34 and other four Armillaria was complex.
Conclusions: These characteristics may be beneficial for establishing a symbiotic relationship with G. elata. These results explore the characteristics of A. gallica Jzi34 from a genomic perspective and provide an important genomic resource for further detailed study of Armillaria. This will help to further study the symbiotic mechanism between A. gallica and G. elata.
Keywords: Armillaria; Gastrodia elata; Genome; Molecular mechanism; Symbionts.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yang CS, Chiu SC, Liu PY, Wu SN, Lai MC, Huang CW. Gastrodin alleviates seizure severity and neuronal excitotoxicities in the rat lithium-pilocarpine model of temporal lobe epilepsy via enhancing GABAergic transmission. J Ethnopharmacol. 2021;269:113751. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113751. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

