Lung Ultrasound in Critical Care and Emergency Medicine: Clinical Review
- PMID: 37218800
- PMCID: PMC10204578
- DOI: 10.3390/arm91030017
Lung Ultrasound in Critical Care and Emergency Medicine: Clinical Review
Abstract
Lung ultrasound has become a part of the daily examination of physicians working in intensive, sub-intensive, and general medical wards. The easy access to hand-held ultrasound machines in wards where they were not available in the past facilitated the widespread use of ultrasound, both for clinical examination and as a guide to procedures; among point-of-care ultrasound techniques, the lung ultrasound saw the greatest spread in the last decade. The COVID-19 pandemic has given a boost to the use of ultrasound since it allows to obtain a wide range of clinical information with a bedside, not harmful, repeatable examination that is reliable. This led to the remarkable growth of publications on lung ultrasounds. The first part of this narrative review aims to discuss basic aspects of lung ultrasounds, from the machine setting, probe choice, and standard examination to signs and semiotics for qualitative and quantitative lung ultrasound interpretation. The second part focuses on how to use lung ultrasound to answer specific clinical questions in critical care units and in emergency departments.
Keywords: acute respiratory failure; lung aeration; lung ultrasound; pleural effusion; pneumonia; pneumothorax; point-of-care ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


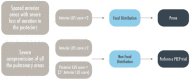
Similar articles
-
Lung Ultrasound for Critically Ill Patients.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019 Mar 15;199(6):701-714. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201802-0236CI. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2019. PMID: 30372119 Review.
-
[Lung Ultrasound for Anesthesia, Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine].Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2019 Feb;54(2):108-127. doi: 10.1055/a-0664-5700. Epub 2019 Feb 15. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2019. PMID: 30769351 Review. German.
-
Ten good reasons to practice ultrasound in critical care.Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2014 Nov-Dec;46(5):323-35. doi: 10.5603/AIT.2014.0056. Anaesthesiol Intensive Ther. 2014. PMID: 25432552 Review.
-
Role of point of care ultrasound in COVID-19 pandemic: what lies beyond the horizon?Med Ultrason. 2020 Nov 18;22(4):461-468. doi: 10.11152/mu-2614. Epub 2020 Jul 22. Med Ultrason. 2020. PMID: 32905568 Review.
-
Prospective Longitudinal Evaluation of Point-of-Care Lung Ultrasound in Critically Ill Patients With Severe COVID-19 Pneumonia.J Ultrasound Med. 2021 Mar;40(3):443-456. doi: 10.1002/jum.15417. Epub 2020 Aug 14. J Ultrasound Med. 2021. PMID: 32797661 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lung ultrasound score and in-hospital mortality of adults with acute respiratory distress syndrome: a meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Jan 29;24(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s12890-023-02826-5. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 38287299 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiogenic Pulmonary Edema in Emergency Medicine.Adv Respir Med. 2023 Oct 13;91(5):445-463. doi: 10.3390/arm91050034. Adv Respir Med. 2023. PMID: 37887077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasound on the Frontlines: Empowering Paramedics with Lung Ultrasound for Dyspnea Diagnosis in Adults-A Pilot Study.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Nov 9;13(22):3412. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13223412. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37998549 Free PMC article.
-
Lung Ultrasound in Critical Care: A Narrative Review.Diagnostics (Basel). 2025 Mar 17;15(6):755. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics15060755. Diagnostics (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40150097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Integrative assessment of congestion in heart failure using ultrasound imaging.Intern Emerg Med. 2025 Jan;20(1):11-22. doi: 10.1007/s11739-024-03755-9. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Intern Emerg Med. 2025. PMID: 39235709 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kasper D., Fauci A., Longo D., Hauser S., Jameson J.L. Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. 19th ed. McGraw-Hill; New York, NY, USA: 2015. pp. 1663–1664.
-
- Mongodi S., Orlando A., Arisi E., Tavazzi G., Santangelo E., Caneva L., Pozzi M., Pariani E., Bettini G., Maggio G., et al. Lung Ultrasound in Patients with Acute Respiratory Failure Reduces Conventional Imaging and Health Care Provider Exposure to COVID-19. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2020;46:2090–2093. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2020.04.033. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

