Specific regulation of mechanical nociception by Gβ5 involves GABA-B receptors
- PMID: 37219953
- PMCID: PMC10371342
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.134685
Specific regulation of mechanical nociception by Gβ5 involves GABA-B receptors
Abstract
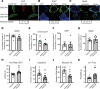
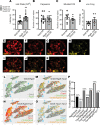
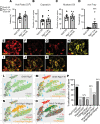
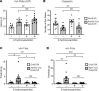
Mechanical, thermal, and chemical pain sensation is conveyed by primary nociceptors, a subset of sensory afferent neurons. The intracellular regulation of the primary nociceptive signal is an area of active study. We report here the discovery of a Gβ5-dependent regulatory pathway within mechanical nociceptors that restrains antinociceptive input from metabotropic GABA-B receptors. In mice with conditional knockout (cKO) of the gene that encodes Gβ5 (Gnb5) targeted to peripheral sensory neurons, we demonstrate the impairment of mechanical, thermal, and chemical nociception. We further report the specific loss of mechanical nociception in Rgs7-Cre+/- Gnb5fl/fl mice but not in Rgs9-Cre+/- Gnb5fl/fl mice, suggesting that Gβ5 might specifically regulate mechanical pain in regulator of G protein signaling 7-positive (Rgs7+) cells. Additionally, Gβ5-dependent and Rgs7-associated mechanical nociception is dependent upon GABA-B receptor signaling since both were abolished by treatment with a GABA-B receptor antagonist and since cKO of Gβ5 from sensory cells or from Rgs7+ cells potentiated the analgesic effects of GABA-B agonists. Following activation by the G protein-coupled receptor Mrgprd agonist β-alanine, enhanced sensitivity to inhibition by baclofen was observed in primary cultures of Rgs7+ sensory neurons harvested from Rgs7-Cre+/- Gnb5fl/fl mice. Taken together, these results suggest that the targeted inhibition of Gβ5 function in Rgs7+ sensory neurons might provide specific relief for mechanical allodynia, including that contributing to chronic neuropathic pain, without reliance on exogenous opioids.
Keywords: G protein–coupled receptors; G proteins; Neuroscience; Pain.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association of Rgs7/Gβ5 complexes with Girk channels and GABAB receptors in hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons.Hippocampus. 2013 Dec;23(12):1231-45. doi: 10.1002/hipo.22161. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Hippocampus. 2013. PMID: 23804514 Free PMC article.
-
Macromolecular composition dictates receptor and G protein selectivity of regulator of G protein signaling (RGS) 7 and 9-2 protein complexes in living cells.J Biol Chem. 2013 Aug 30;288(35):25129-25142. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462283. Epub 2013 Jul 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23857581 Free PMC article.
-
The Gbeta5-RGS7 complex selectively inhibits muscarinic M3 receptor signaling via the interaction between the third intracellular loop of the receptor and the DEP domain of RGS7.Biochemistry. 2009 Mar 17;48(10):2282-9. doi: 10.1021/bi801989c. Biochemistry. 2009. PMID: 19182865 Free PMC article.
-
R9AP and R7BP: traffic cops for the RGS7 family in phototransduction and neuronal GPCR signaling.Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009 Jan;30(1):17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2008.10.002. Epub 2008 Nov 29. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19042037 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure, function, and localization of Gβ5-RGS complexes.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009;86:157-203. doi: 10.1016/S1877-1173(09)86006-7. Epub 2009 Oct 7. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2009. PMID: 20374716 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The association of GNB5 with Alzheimer disease revealed by genomic analysis restricted to variants impacting gene function.Am J Hum Genet. 2024 Mar 7;111(3):473-486. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2024.01.005. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Am J Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 38354736 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

