Computational Study of Base-Catalyzed Thiohemiacetal Decomposition in Pseudomonas mevalonii HMG-CoA Reductase
- PMID: 37219997
- PMCID: PMC11607680
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.2c08969
Computational Study of Base-Catalyzed Thiohemiacetal Decomposition in Pseudomonas mevalonii HMG-CoA Reductase
Abstract
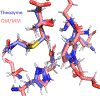
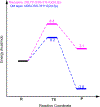
Thiohemiacetals are key intermediates in the active sites of many enzymes catalyzing a variety of reactions. In the case of Pseudomonas mevalonii 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase (PmHMGR), this intermediate connects the two hydride transfer steps where a thiohemiacetal is the product of the first hydride transfer and its breakdown forms the substrate of the second one, serving as the intermediate during cofactor exchange. Despite the many examples of thiohemiacetals in a variety of enzymatic reactions, there are few studies that detail their reactivity. Here, we present computational studies on the decomposition of the thiohemiacetal intermediate in PmHMGR using both QM-cluster and QM/MM models. This reaction mechanism involves a proton transfer from the substrate hydroxyl to an anionic Glu83 followed by a C-S bond elongation stabilized by a cationic His381. The reaction provides insight into the varying roles of the residues in the active site that favor this multistep mechanism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


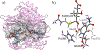
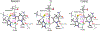
Similar articles
-
A novel role for coenzyme A during hydride transfer in 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase.Biochemistry. 2013 Aug 6;52(31):5195-205. doi: 10.1021/bi400335g. Epub 2013 Jul 24. Biochemistry. 2013. PMID: 23802607 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of the principal catalytically important acidic residue of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase.J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 15;265(35):21634-41. J Biol Chem. 1990. PMID: 2123872
-
Identification of the catalytically important histidine of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase.J Biol Chem. 1992 Jul 25;267(21):15064-70. J Biol Chem. 1992. PMID: 1634543
-
The 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme-A (HMG-CoA) reductases.Genome Biol. 2004;5(11):248. doi: 10.1186/gb-2004-5-11-248. Epub 2004 Nov 1. Genome Biol. 2004. PMID: 15535874 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brief history of glyoxalase I and what we have learned about metal ion-dependent, enzyme-catalyzed isomerizations.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001 Mar 1;387(1):1-10. doi: 10.1006/abbi.2000.2253. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2001. PMID: 11368170 Review.
Cited by
-
pH-dependent reaction triggering in PmHMGR crystals for time-resolved crystallography.Biophys J. 2024 Mar 5;123(5):622-637. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2024.02.003. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Biophys J. 2024. PMID: 38327055 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrolysis Reactions of p-Nitrophenyl Trifluoroacetate and S-Ethyl Trifluorothioacetate.Molecules. 2025 Jan 11;30(2):268. doi: 10.3390/molecules30020268. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39860138 Free PMC article.
-
Post-Translational Modifications to Cysteine Residues in Plant Proteins and Their Impact on the Regulation of Metabolism and Signal Transduction.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 12;25(18):9845. doi: 10.3390/ijms25189845. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burini RC; Kano HT; Yu Y-M The Life Evolution on the Sulfur Cycle: From Ancient Elemental Sulfur Reduction and Sulfide Oxidation to the Contemporary Thiol-Redox Challenges. In Glutathione in Health and Disease; IntechOpen: 2018; pp 9–26.
-
- Mueller EG Trafficking in Persulfides: Delivering Sulfur in Biosynthetic Pathways. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 185–194. - PubMed
-
- Richter M Functional Diversity of Organic Molecule Enzyme Cofactors. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 1324–1345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

