Management of Complex Crown Fractures: A Case Series
- PMID: 37220460
- PMCID: PMC10200002
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.37907
Management of Complex Crown Fractures: A Case Series
Abstract
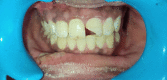
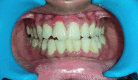
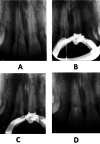
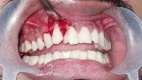
Maxillary teeth are most vulnerable to fracture due to trauma. An effective treatment plan for an anterior teeth fracture not only improves function and appearance but also benefits the patient psychologically. The reattachment of the fragmented tooth is one of the best treatment methods for such condition. It is considered as a better treatment option because it is uncomplicated, aesthetic, and preserves the dental structure. To achieve a positive prognosis, patient cooperation and awareness about the treatment are essential. This article includes three case reports that illustrate the management of complex maxillary anterior teeth fractures wherein the reattachment of the fractured tooth segments was undertaken.
Keywords: complicated fracture; crown fracture; maxillary anterior teeth; reattachment; trauma.
Copyright © 2023, Lakshmaiah et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
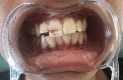

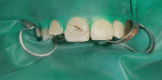
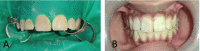
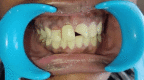





References
-
- Etiology and pathogenesis of traumatic dental injuries. A clinical study of 1,298 cases. Andreasen JO. Scand J Dent Res. 1970;78:329–342. - PubMed
-
- Andreasen JO, Andreasen FM, Andersson L. Oxford, UK: Blackwell. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2018. Textbook and Color Atlas of Traumatic Injuries to the Teeth, 5th Edition.
-
- Changing concepts in fracture reattachment of teeth—a case series. Divakar HD, Nayak M, Shetty R. Endodontology. 2009;21:48–54.
-
- Crown fractures in the permanent dentition: pulpal and restorative considerations. Olsburgh S, Jacoby T, Krejci I. Dent Traumatol. 2002;18:103–115. - PubMed
-
- Tooth fragment reattachment: a case report. Taguchi CM, Bernardon JK, Zimmermann G, Baratieri LN. Oper Dent. 2015;40:227–234. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
