The Zoige pioneer plant Leymus secalinus has different endophytic bacterial community structures to adapt to environmental conditions
- PMID: 37220526
- PMCID: PMC10200098
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj.15363
The Zoige pioneer plant Leymus secalinus has different endophytic bacterial community structures to adapt to environmental conditions
Abstract
Background: Leymus secalinus is a pioneer plant grown in the Zoige desertified alpine grassland and it is also one of the dominant plant species used for environmental remediation. L. secalinus plays a large role in vegetation reconstruction in sandy land, but the abundance and diversity of its endophytes have not yet been investigated.
Objectives: This study was performed to investigate the changes in the endophytic bacterial community structure of L. secalinus under different ecological environments and to analyze the effects of environmental changes and different plant tissues on the L. secalinus endophytic bacteria.
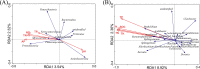
Methods: Leaf, stem, and root tissue samples of L. secalinus were collected from Zoige Glassland (Alpine sandy land) and an open field nursery (Control). DNA was extracted and the 16S ribosomal DNA was amplified. The sequence library was sequenced on an Illumina MiSeq platform and clustered by operational taxonomic units (OTUs). α-diversity and β-diversity analyses, species diversity analyses, functional prediction, and redundancy (RDA) analyses for the soil physicochemical properties were conducted.
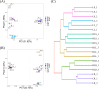
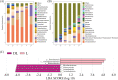
Results: α-diversity and β-diversity analyses showed that the endophytic bacteria in L. secalinus varied in different areas and tissues. The abundance of Allorhizobium-Neorhizobium-Pararhizobium-Rhizobium, which is related to nitrogen fixation, increased significantly in the L. secalinus found in the Zoige Grassland.Moreover, the abundance of nutrition metabolism and anti-stress abilities increased in functional prediction in the desert samples. The soil physicochemical properties had an insignificant influence on bacterial diversity.
Conclusion: The changes in the endophytic bacterial community structure in L. secalinus were significant and were caused by environmental alterations and plant choice. The endophytic bacteria in L. secalinus grown in alpine sandy land may have greater anti-stress properties and the ability to fix nitrogen, which has potential value in environmental remediation and agricultural production.
Keywords: 16S rRNA gene sequencing; Endophytic bacterium; Leymus secalinus; Nitrogen fixation; Vegetation remediation; Zoige alpine grassland.
©2023 Xia et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Short-term warming and N deposition alter the photosynthetic pigments trade-off in leaves of Leymus secalinus growing in different alpine grassland habitats on Qinghai-Tibetan plateau.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Feb;30(6):15282-15292. doi: 10.1007/s11356-022-22805-3. Epub 2022 Sep 27. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 36166121
-
Growth and physiological metabolic regulation mechanisms of the dominant plant Leymus secalinus in alpine meadow under nitrogen deposition.Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024 Nov;216:109150. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2024.109150. Epub 2024 Sep 24. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39342658
-
Remediation of blowouts by clonal plants in Maqu degraded alpine grasslands of northwest China.J Plant Res. 2017 Mar;130(2):291-299. doi: 10.1007/s10265-016-0884-2. Epub 2016 Dec 1. J Plant Res. 2017. PMID: 27909827
-
Characterization of endophytic bacteriome diversity and associated beneficial bacteria inhabiting a macrophyte Eichhornia crassipes.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 19;14:1176648. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1176648. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37404529 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of grassland management regimes on bacterial endophyte diversity differs with grass species.Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016 Apr;62(4):323-9. doi: 10.1111/lam.12551. Epub 2016 Mar 9. Lett Appl Microbiol. 2016. PMID: 26834040
Cited by
-
Microbial communities of Schisandra sphenanthera Rehd. et Wils. and the correlations between microbial community and the active secondary metabolites.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 26;12:e17240. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17240. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38685939 Free PMC article.
-
Plant Growth-Promoting Effect and Complete Genomic Sequence Analysis of the Beneficial Rhizosphere Streptomyces sp. GD-4 Isolated from Leymus secalinus.Microorganisms. 2025 Jan 27;13(2):286. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13020286. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40005653 Free PMC article.
-
MaxEnt-Based Predictions of Suitable Potential Distribution of Leymus secalinus Under Current and Future Climate Change.Plants (Basel). 2025 Jan 20;14(2):293. doi: 10.3390/plants14020293. Plants (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39861646 Free PMC article.
-
Endophytic Bacteria with Potential Antimicrobial Activity Isolated from Theobroma cacao in Brazilian Amazon.Microorganisms. 2025 Jul 18;13(7):1686. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13071686. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40732195 Free PMC article.
-
A finding of potential coexisting bacteria and characterization of the bacterial communities in the fruiting body of Sarcodon aspratus.Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024 Oct;69(5):1137-1144. doi: 10.1007/s12223-024-01189-6. Epub 2024 Aug 19. Folia Microbiol (Praha). 2024. PMID: 39160370
References
-
- Banik A, Dash GK, Swain P, Kumar U, Mukhopadhyay SK, Dangar TK. Application of rice (Oryza sativa L.) root endophytic diazotrophic Azotobacter sp. strain Avi2 (MCC 3432) can increase rice yield under green house and field condition. Microbiological Research. 2019;219:56–65. doi: 10.1016/j.micres.2018.11.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

