Sarcoidosis of the lacrimal gland: the prominence of the differential diagnosis
- PMID: 37221006
- PMCID: PMC10230888
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2022-253880
Sarcoidosis of the lacrimal gland: the prominence of the differential diagnosis
Abstract
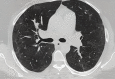
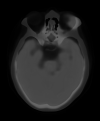
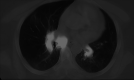
Sarcoidosis is a multisystem disease that can involve any organ; lungs, lymph nodes and skin are the most involved. Compatible clinical and imaging features, the identification of non-caseous granulomas on biopsy and the exclusion of other causes of granulomatous disorders help formulate the diagnosis of sarcoidosis. A bilateral symmetrical hilar lymphadenopathy together with the typical perilymphatic distribution of nodules is typically visible on high-resolution CT.The average age is 48 years. Ocular sarcoidosis is not rare, it is reported in 25% of cases. Half of the sarcoidosis patients resolve spontaneously; treatment is only indicated in cases with severe symptoms or signs of organ damage. Classical treatments are based on the use of corticosteroids and immunosuppressive therapies, sometimes combined.
Keywords: COVID-19; Interstitial lung disease; Oral and maxillofacial surgery.
© BMJ Publishing Group Limited 2023. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
