Structural basis for RNA-duplex unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase DbpA
- PMID: 37221012
- PMCID: PMC10573307
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.079582.123
Structural basis for RNA-duplex unwinding by the DEAD-box helicase DbpA
Abstract
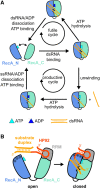
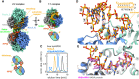
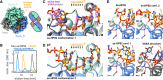
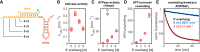
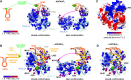
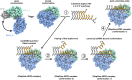
DEAD-box RNA helicases are implicated in most aspects of RNA biology, where these enzymes unwind short RNA duplexes in an ATP-dependent manner. During the central step of the unwinding cycle, the two domains of the helicase core form a distinct closed conformation that destabilizes the RNA duplex, which ultimately leads to duplex melting. Despite the importance of this step for the unwinding process no high-resolution structures of this state are available. Here, I used nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography to determine structures of the DEAD-box helicase DbpA in the closed conformation, complexed with substrate duplexes and single-stranded unwinding product. These structures reveal that DbpA initiates duplex unwinding by interacting with up to three base-paired nucleotides and a 5' single-stranded RNA duplex overhang. These high-resolution snapshots, together with biochemical assays, rationalize the destabilization of the RNA duplex and are integrated into a conclusive model of the unwinding process.
Keywords: DEAD-box helicase; NMR spectroscopy; RNA; molecular mechanism; ribosome biogenesis.
© 2023 Wurm; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures


References
-
- Afonine PV, Grosse-Kunstleve RW, Echols N, Headd JJ, Moriarty NW, Mustyakimov M, Terwilliger TC, Urzhumtsev A, Zwart PH, Adams PD. 2012. Towards automated crystallographic structure refinement with phenix.refine. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 68: 352–367. 10.1107/S0907444912001308 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
