Cysteine tRNA acts as a stop codon readthrough-inducing tRNA in the human HEK293T cell line
- PMID: 37221013
- PMCID: PMC10573299
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.079688.123
Cysteine tRNA acts as a stop codon readthrough-inducing tRNA in the human HEK293T cell line
Abstract
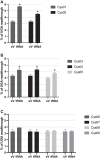
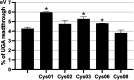
Under certain circumstances, any of the three termination codons can be read through by a near-cognate tRNA; i.e., a tRNA whose two out of three anticodon nucleotides base pair with those of the stop codon. Unless programed to synthetize C-terminally extended protein variants with expanded physiological roles, readthrough represents an undesirable translational error. On the other side of a coin, a significant number of human genetic diseases is associated with the introduction of nonsense mutations (premature termination codons [PTCs]) into coding sequences, where stopping is not desirable. Here, the tRNA's ability to induce readthrough opens up the intriguing possibility of mitigating the deleterious effects of PTCs on human health. In yeast, the UGA and UAR stop codons were described to be read through by four readthrough-inducing rti-tRNAs-tRNATrp and tRNACys, and tRNATyr and tRNAGln, respectively. The readthrough-inducing potential of tRNATrp and tRNATyr was also observed in human cell lines. Here, we investigated the readthrough-inducing potential of human tRNACys in the HEK293T cell line. The tRNACys family consists of two isoacceptors, one with ACA and the other with GCA anticodons. We selected nine representative tRNACys isodecoders (differing in primary sequence and expression level) and tested them using dual luciferase reporter assays. We found that at least two tRNACys can significantly elevate UGA readthrough when overexpressed. This indicates a mechanistically conserved nature of rti-tRNAs between yeast and human, supporting the idea that they could be used in the PTC-associated RNA therapies.
Keywords: cysteine tRNA; near-cognate tRNA; readthrough-inducing tRNA; stop codon readthrough; translation.
© 2023 Valášek et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Yeast applied readthrough inducing system (YARIS): an invivo assay for the comprehensive study of translational readthrough.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jul 9;47(12):6339-6350. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz346. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 31069379 Free PMC article.
-
Extended stop codon context predicts nonsense codon readthrough efficiency in human cells.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 20;15(1):2486. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-46703-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38509072 Free PMC article.
-
Rules of UGA-N decoding by near-cognate tRNAs and analysis of readthrough on short uORFs in yeast.RNA. 2016 Mar;22(3):456-66. doi: 10.1261/rna.054452.115. Epub 2016 Jan 12. RNA. 2016. PMID: 26759455 Free PMC article.
-
Translational readthrough potential of natural termination codons in eucaryotes--The impact of RNA sequence.RNA Biol. 2015;12(9):950-8. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2015.1068497. RNA Biol. 2015. PMID: 26176195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Misreading of termination codons in eukaryotes by natural nonsense suppressor tRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 2001 Dec 1;29(23):4767-82. doi: 10.1093/nar/29.23.4767. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001. PMID: 11726686 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ribosomal A-site interactions with near-cognate tRNAs drive stop codon readthrough.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025 Apr;32(4):662-674. doi: 10.1038/s41594-024-01450-z. Epub 2025 Jan 13. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 39806023
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
