Patient Characteristics, Testing and Treatment Patterns, and Outcomes in EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multinational, Real-World Study
- PMID: 37221352
- PMCID: PMC10204685
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-023-02530-0
Patient Characteristics, Testing and Treatment Patterns, and Outcomes in EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multinational, Real-World Study
Abstract
Introduction: Treatment landscape for advanced/metastatic NSCLC (aNSCLC) has evolved considerably over the past few decades with the advent of targeted therapies for epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated (EGFRm+) aNSCLC treatment. This study described real-world patient and disease characteristics, treatment and practice patterns, and clinical, economic, and patient-reported outcomes (PROs) in patients with EGFRm+ aNSCLC.
Methods: Data were derived from the Adelphi NSCLC Disease Specific Programme™ (DSP™), a point-in-time survey conducted between July and December 2020. The survey included oncologists and pulmonologists, and their consulting patients (with physician-confirmed EGFRm+ aNSCLC) from nine countries: the US, Brazil, the UK, Italy, France, Spain, Germany, Japan, and Taiwan. All analyses were descriptive.
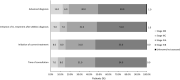
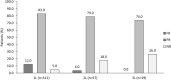
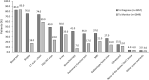
Results: Overall, 542 physicians reported data for 2857 patients (mean age 65.6 years), and most patients were female (56.0%), white (61.0%), and had stage IV disease at initial diagnosis (76.0%), and adenocarcinoma histology (89.0%). Most patients received EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) therapy in first- (91.0%), second- (74.0%), and third-line (67.0%). The most common tumor samples and methods for EGFR detection were EGFR-specific mutation detection tests (44.0%) and core needle biopsy (56.0%). Median time to next treatment was 14.0 (IQR 8.0-22.0) months and disease progression was the main physician-reported reason for early discontinuation. The most common physician-reported disease symptoms were cough (51.0%), fatigue (37.0%), and dyspnea (33.0%). In patients assessed for PROs, mean EQ-5D-5L index and FACT-L health utility scores were 0.71 and 83.5, respectively. On average, patients lost 10.6 h of work/week for approximately 29.2 weeks due to EGFRm+ aNSCLC.
Conclusion: This real-world multinational data set showed that most patients with EGFRm+ aNSCLC were treated per the country relevant clinical guidelines, with progression as the main reason for early treatment discontinuation. For the included countries, these findings may offer a useful benchmark for decision makers to determine future allocation of healthcare resources for patients with EGFRm+ aNSCLC.
Keywords: Advanced non-small cell lung cancer; Disease Specific Programme™; EGFR mutation; Patient-reported outcomes; Point-in-time; Real-world; Survey; Treatment patterns.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Cliff Molife, Katherine B Winfree, Sangmi Kim, Kaisa-Leena Taipale and Tarun Puri are employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. Cameron Forshaw and Hollie Bailley are employees at Adelphi Real World who received funding from Eli Lilly and Company for this analysis. Publication of study results was not contingent on the subscriber’s approval or censorship of the manuscript. Yulia D’yachkova is a former employee of Eli Lilly and Company.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Usage of epidermal growth factor mutation testing and impact on treatment patterns in non-small cell lung cancer: An international observational study.Lung Cancer. 2023 Jan;175:47-56. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2022.11.009. Epub 2022 Nov 17. Lung Cancer. 2023. PMID: 36455396
-
Real-World Patient Characteristics, Treatment Patterns, and Mutation Testing Patterns Among US Patients with Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Mutations.Adv Ther. 2022 Jul;39(7):3347-3360. doi: 10.1007/s12325-022-02189-z. Epub 2022 Jun 8. Adv Ther. 2022. PMID: 35674970
-
Real-world health utility scores and toxicities to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in epidermal growth factor receptor mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer.Cancer Med. 2019 Dec;8(18):7542-7555. doi: 10.1002/cam4.2603. Epub 2019 Oct 24. Cancer Med. 2019. PMID: 31650705 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing the sequencing of tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) in epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation-positive non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Lung Cancer. 2019 Nov;137:113-122. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2019.09.017. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Lung Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31568888 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ideal sequencing in Stage IV epidermal growth factor receptor mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer.Indian J Cancer. 2022 Mar;59(Supplement):S80-S89. doi: 10.4103/ijc.IJC_50_21. Indian J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35343193 Review.
Cited by
-
Rebiopsy Enhances Survival with Afatinib vs. Osimertinib in EGFR Exon 19 Deletion Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Multicenter Study in Taiwan.Curr Oncol. 2025 Jan 10;32(1):36. doi: 10.3390/curroncol32010036. Curr Oncol. 2025. PMID: 39851952 Free PMC article.
-
Quality of Life Evaluation in Patients with Follicular Cell Lymphoma: A Real-World Study in Europe and the United States.Adv Ther. 2024 Aug;41(8):3342-3361. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-02882-1. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 38976122 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Cancer, key facts. 2022. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer. Accessed 7 Dec 2022.
-
- Cancer.net. Lung cancer - non-small cell: statistics. 2022. https://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/lung-cancer-non-small-cell/statistics. Accessed 7 Dec 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

