Alterations in retrobulbar haemodynamics in thyroid eye disease
- PMID: 37221361
- PMCID: PMC10686394
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-023-02580-2
Alterations in retrobulbar haemodynamics in thyroid eye disease
Abstract
Purpose: To study the orbital perfusion parameters of ophthalmic artery (OA) and central retinal artery (CRA) in inactive TED and the changes following surgical decompression.
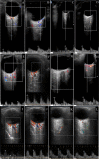
Methods: Non-randomised clinical trial. 24 inactive moderate-to-severe TED orbits of 24 euthyroid cases underwent surgical decompression and examined again at 3 months. The peak systolic velocity (PSV), end-diastolic velocity (EDV), and resistivity index (RI) of OA and CRA were evaluated using colour doppler imaging and normative database was established using 18 healthy controls.
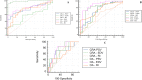
Results: The mean age was 39.38 ± 12.56 years and male: female ratio was 1: 1.18. Intraocular pressure was higher, and CRA-PSV, CRA-RI, OA-PSV, and OA-EDV were lower in TED in comparison to heathy orbits. The CRA-PSV, CRA-EDV, OA-PSV, and OA-EDV negatively correlated with proptosis and duration of thyroid disease. The area under curve of OA-PSV (95% CI:0.964-1.000, p < 0.001) and OA-EDV (95% CI:0.699-0.905, p < 0.001) helped in differentiating TED orbits from HC, and in predicting the severity of disease. Post decompression, CRA-PSV, CRA-EDV, OA-PSV, and OA-EDV improved, with decrease in CRA-RI and OA-RI in both lipogenic and MO.
Conclusions: The orbital perfusion is reduced in inactive TED. The changes in OA flow velocities can help in differentiating inactive TED from healthy orbits and progression of TED. Sequential orbital CDI of OA and CRA can serve as an objective tool for case selection and monitoring response to surgical decompression.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to The Royal College of Ophthalmologists.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of orbital hemodynamic changes in primary open angle glaucoma by color Doppler imaging.J Fr Ophtalmol. 2023 Nov;46(9):1061-1068. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2023.03.018. Epub 2023 Aug 23. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2023. PMID: 37625998
-
Retrobulbar hemodynamic parameters in pseudoexfoliation syndrome and pseudoexfoliative glaucoma.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008 Sep;246(9):1341-9. doi: 10.1007/s00417-008-0841-4. Epub 2008 May 20. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2008. PMID: 18491127
-
Doppler ultrasonographic measurement of short-term effects of valsalva maneuver on retrobulbar blood flow.J Clin Ultrasound. 2017 Nov 12;45(9):551-555. doi: 10.1002/jcu.22487. Epub 2017 Apr 25. J Clin Ultrasound. 2017. PMID: 28440860
-
Color Doppler imaging of orbital vasculature before and after orbital decompression in thyroid eye disease.Orbit. 2019 Jun;38(3):173-179. doi: 10.1080/01676830.2018.1513537. Epub 2018 Aug 24. Orbit. 2019. PMID: 30142011
-
Orbital and ocular perfusion in thyroid eye disease.Surv Ophthalmol. 2023 May-Jun;68(3):481-506. doi: 10.1016/j.survophthal.2023.01.003. Epub 2023 Jan 18. Surv Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 36681278 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessment of choroidal perfusion indices in thyroid eye disease by using optical coherence tomography.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024 Nov 1;72(11):1639-1644. doi: 10.4103/IJO.IJO_3315_23. Epub 2024 May 20. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38767537 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rundle FF, Wilson CW. Development and course of exophthalmos and ophthalmoplegia in Graves’ disease with special reference to the effect of thyroidectomy. Clin Sci. 1945;5:177–94. - PubMed
-
- Nakase Y, Osanai T, Yoshikawa K, Inoue Y. Color Doppler imaging of orbital venous flow in dysthyroid optic neuropathy. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 1994;38:80–6. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

