Smart IoT in Breast Cancer Detection Using Optimal Deep Learning
- PMID: 37221422
- PMCID: PMC10406774
- DOI: 10.1007/s10278-023-00834-9
Smart IoT in Breast Cancer Detection Using Optimal Deep Learning
Abstract
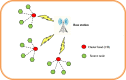
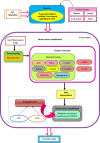
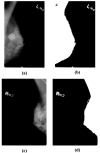
IoT in healthcare systems is currently a viable option for providing higher-quality medical care for contemporary e-healthcare. Using an Internet of Things (IoT)-based smart healthcare system, a trustworthy breast cancer classification method called Feedback Artificial Crow Search (FACS)-based Shepherd Convolutional Neural Network (ShCNN) is developed in this research. To choose the best routes, the secure routing operation is first carried out using the recommended FACS while taking fitness measures such as distance, energy, link quality, and latency into account. Then, by merging the Crow Search Algorithm (CSA) and Feedback Artificial Tree, the produced FACS is put into practice (FAT). After the completion of routing phase, the breast cancer categorization process is started at the base station. The feature extraction step is then introduced to the pre-processed input mammography image. As a result, it is possible to successfully get features including area, mean, variance, energy, contrast, correlation, skewness, homogeneity, Gray Level Co-occurrence Matrix (GLCM), and Local Gabor Binary Pattern (LGBP). The quality of the image is next enhanced through data augmentation, and finally, the developed FACS algorithm's ShCNN is used to classify breast cancer. The performance of FACS-based ShCNN is examined using six metrics, including energy, delay, accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and True Positive Rate (TPR), with the maximum energy of 0.562 J, the least delay of 0.452 s, the highest accuracy of 91.56%, the higher sensitivity of 96.10%, the highest specificity of 91.80%, and the maximum TPR of 99.45%.
Keywords: And Shepherd Convolutional Neural Network; Breast cancer; Crow Search Algorithm; Feedback Artificial Tree; Internet of Things.
© 2023. The Author(s) under exclusive licence to Society for Imaging Informatics in Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Shende, Dipali K. and Yogesh S. Angal, and S.C. Patil. “An Iterative CrowWhale-Based Optimization Model for Energy-Aware Multicast Routing in IoT,” International Journal of Information Security and Privacy (IJISP) vol.16, no.1, pp.1–24, 2022.
-
- Shende, Dipali & Sonavane, Shefali & Angal, Yogesh, “A Comprehensive Survey of the Routing Schemes for IoT applications”, Scalable Computing: Practice and Experience, vol.no. 21, pp.203–216, 2020.
-
- Jaglan, P., Dass, R. and Duhan, M., “Breast cancer detection techniques: issues and challenges”, Journal of The Institution of Engineers (India): Series B, vol.100, no.4, pp.379–386, August 2019.
-
- K. Al-Saedi, M. Al-Emran, E. Abusham and S. A. El Rahman, “Mobile Payment Adoption: A Systematic Review of the UTAUT Model,” 2019 International Conference on Fourth Industrial Revolution (ICFIR), 2019, pp. 1–5,2019.
-
- V. Rupapara, M. Narra, N. K. Gunda, S. Gandhi and K. R. Thipparthy, “Maintaining Social Distancing in Pandemic Using Smartphones With Acoustic Waves,” in IEEE Transactions on Computational Social Systems, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 605–611, 2022,
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

