An integrative review of nonobvious puzzles of cellular and molecular cardiooncology
- PMID: 37221467
- PMCID: PMC10207659
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-023-00451-y
An integrative review of nonobvious puzzles of cellular and molecular cardiooncology
Abstract
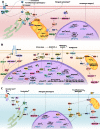
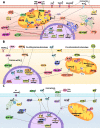
Oncologic patients are subjected to four major treatment types: surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. All nonsurgical forms of cancer management are known to potentially violate the structural and functional integrity of the cardiovascular system. The prevalence and severity of cardiotoxicity and vascular abnormalities led to the emergence of a clinical subdiscipline, called cardiooncology. This relatively new, but rapidly expanding area of knowledge, primarily focuses on clinical observations linking the adverse effects of cancer therapy with deteriorated quality of life of cancer survivors and their increased morbidity and mortality. Cellular and molecular determinants of these relations are far less understood, mainly because of several unsolved paths and contradicting findings in the literature. In this article, we provide a comprehensive view of the cellular and molecular etiology of cardiooncology. We pay particular attention to various intracellular processes that arise in cardiomyocytes, vascular endothelial cells, and smooth muscle cells treated in experimentally-controlled conditions in vitro and in vivo with ionizing radiation and drugs representing diverse modes of anti-cancer activity.
Keywords: Cardiac cells; Cardiooncology; Cardiotoxicity; Vascular cells.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cellular model systems to study cardiovascular injury from chemotherapy.J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021 May;51(4):890-896. doi: 10.1007/s11239-020-02299-x. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2021. PMID: 33051807 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Challenges and solutions in management of cardiotoxicity induced by checkpoint inhibitors.Klin Onkol. 2020 Spring;33(5):350-355. doi: 10.14735/amko2020350. Klin Onkol. 2020. PMID: 33108879 English.
-
Cancer Treatment-Related Cardiovascular Toxicity in Gynecologic Malignancies: JACC: CardioOncology State-of-the-Art Review.JACC CardioOncol. 2023 Apr 18;5(2):159-173. doi: 10.1016/j.jaccao.2023.02.002. eCollection 2023 Apr. JACC CardioOncol. 2023. PMID: 37144116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunotherapy-Associated Cardiotoxicity of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors and Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cell Therapy: Diagnostic and Management Challenges and Strategies.Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021 Jan 22;23(3):11. doi: 10.1007/s11886-021-01440-3. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021. PMID: 33483873 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Cardiotoxicity With Stem Cell-based Strategies.Clin Ther. 2020 Oct;42(10):1892-1910. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2020.08.012. Epub 2020 Sep 13. Clin Ther. 2020. PMID: 32938533 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibition of SQSTM1 S403 phosphorylation facilitates the aggresome formation of ubiquitinated proteins during proteasome dysfunction.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Oct 24;28(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00500-6. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37872526 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupted cardiac fibroblast BCAA catabolism contributes to diabetic cardiomyopathy via a periostin/NAP1L2/SIRT3 axis.Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023 Nov 22;28(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s11658-023-00510-4. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 2023. PMID: 37993768 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Majeed H, Gupta V. Adverse effects of radiation therapy. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL)2022. - PubMed
-
- Strongman H, Gadd S, Matthews A, Mansfield KE, Stanway S, Lyon AR, et al. Medium and long-term risks of specific cardiovascular diseases in survivors of 20 adult cancers: a population-based cohort study using multiple linked UK electronic health records databases. Lancet. 2019;394(10203):1041–1054. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31674-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

