Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
- PMID: 37221526
- PMCID: PMC10203667
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-023-15763-z
Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Abstract
Background: The outcomes of education and counseling by medical professionals for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are unclear. This study examined the effects of the Chronic Disease Management Program (CDMP), a health insurance fee-for-service benefit, on the incidence of diabetic complications in patients newly diagnosed with T2DM using the National Health Insurance data.
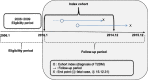
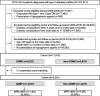
Methods: Patients newly diagnosed with T2DM aged ≥ 20 years from 2010 to 2014 were followed up until 2015. Selection bias was minimized using propensity score matching. A stratified Cox proportional hazards model was used to analyze the association between the CDMP and the risk of incident diabetic complications. Subgroup analysis was performed for patients with high medication adherence, which was indicated by a medication possession ratio (MPR) ≥ 80.
Results: Among the 11,915 patients with T2DM in the cohort, 4,617 were assigned to the CDMP and non-CDMP group each. The CDMP helped reduce the overall and microvascular risks of complications compared to the non-CDMP group; however, the protective effect against macrovascular complications was only observed in those aged ≥ 40 years. Subgroup analysis of the group aged ≥ 40 years with high adherence (an MPR ≥ 80) showed that the CDMP effectively reduced the incidence of micro- and macrovascular complications.
Conclusions: Effective management of T2DM is crucial in preventing complications in patients with the condition, and includes regular monitoring and adjustment of treatment by qualified physicians. Nevertheless, long-term prospective studies on the effects of CDMP are required to confirm this finding.
Keywords: Chronic disease management program; Diabetes complications; Health education; Retrospective studies; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of the chronic disease management program for appropriateness of medication adherence and persistence in hypertension and type-2 diabetes patients in Korea.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(14):e6577. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006577. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28383439 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of pay for performance on risk incidence of hip fracture in type 2 diabetic patients: a nationwide population-based cohort study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Mar;99(12):e19592. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019592. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32195973 Free PMC article.
-
The association between participation in a pay-for-performance program and macrovascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes in Taiwan: A nationwide population-based cohort study.Prev Med. 2016 Apr;85:53-59. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2015.12.013. Epub 2015 Dec 29. Prev Med. 2016. PMID: 26740347
-
The risk of hip fractures in individuals over 50 years old with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes - A longitudinal nationwide population-based study.Bone. 2021 Jan;142:115691. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2020.115691. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Bone. 2021. PMID: 33069920
-
Issues surrounding tight glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Ann Pharmacother. 1998 Sep;32(9):896-905. doi: 10.1345/aph.17375. Ann Pharmacother. 1998. PMID: 9762378 Review.
Cited by
-
Characteristics and needs of physical and mental health among older adult individuals with disabilities under the background of smart healthcare: according to data from the China family panel studies.Front Public Health. 2025 Feb 21;13:1475466. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1475466. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40061462 Free PMC article.
-
Downsizing chronic disease management programs for type 2 diabetes patients during the COVID-19 pandemic: changes in healthcare utilization patterns.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jun 11;12:1490175. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1490175. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40568212 Free PMC article.
-
Recognition of Traumatic Brain Injury as a Chronic Condition: A Commentary.J Neurotrauma. 2024 Dec;41(23-24):2602-2605. doi: 10.1089/neu.2024.0356. Epub 2024 Sep 25. J Neurotrauma. 2024. PMID: 39276117 Review.
References
-
- IDF . IDF Diabetes Atlas 2021–10th edition. Brussels, Belgium: International Diabetes Federation (IDF); 2021. - PubMed
-
- Litwak L, Goh SY, Hussein Z, Malek R, Prusty V, Khamseh ME. Prevalence of diabetes complications in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with baseline characteristics in the multinational A1chieve study. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2013;5(1):57. doi: 10.1186/1758-5996-5-57. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical