Assessment of equity and efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging services in Henan Province, China
- PMID: 37221536
- PMCID: PMC10204287
- DOI: 10.1186/s12962-023-00440-0
Assessment of equity and efficiency of magnetic resonance imaging services in Henan Province, China
Abstract
Background: By evaluating equity and effectiveness, this study provides evidence-based knowledge for scientific decision-making and the optimization of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) configuration and utilization at the provincial level.
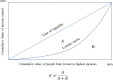
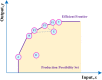
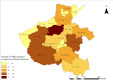
Methods: Using data from 2017, we applied a Gini coefficient to analyze the equity of MRI services in 11 sample cities in Henan province. An agglomeration degree was then applied to measure equity from the perspective of population and geography, and a data envelopment analysis was used to evaluate MRI efficiency.
Results: The overall Gini coefficient of MRI allocation by population in the 11 sample cities is 0.117; however, equity varies considerably among the sample cities. The sample's comprehensive efficiency is only 0.732, indicating the overall ineffectiveness of provincial MRI utilization. The pure technical and scale efficiencies of four sample cities are below 1, indicating lower MRI effectiveness than the rest.
Conclusions: Although the overall equity of configuration at the provincial level is relatively good, equity varies at the municipal level. Our results demonstrate a low MRI utilization efficiency; accordingly, policymakers should dynamically adjust the policy based on equity and efficiency.
Keywords: Agglomeration; Data envelopment analysis (DEA); Efficiency; Equity; Gini coefficient; Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no competing of interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Equity and efficiency of health resource allocation in Sichuan Province, China.BMC Health Serv Res. 2024 Nov 20;24(1):1439. doi: 10.1186/s12913-024-11946-5. BMC Health Serv Res. 2024. PMID: 39568019 Free PMC article.
-
Equity and efficiency of health resource allocation in township health centers in Sichuan Province, China.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 5;19(3):e0299988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299988. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38442112 Free PMC article.
-
Equity and efficiency of maternal and child health resources allocation in Hunan Province, China.BMC Health Serv Res. 2020 Apr 15;20(1):300. doi: 10.1186/s12913-020-05185-7. BMC Health Serv Res. 2020. PMID: 32293425 Free PMC article.
-
Equity and efficiency of health care resource allocation in Jiangsu Province, China.Int J Equity Health. 2020 Nov 27;19(1):211. doi: 10.1186/s12939-020-01320-2. Int J Equity Health. 2020. PMID: 33246458 Free PMC article.
-
Efficiency analysis of oral health resource allocation in public medical institutions in Yunnan Province at the end of the 13th five-year plan in China.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 1;25(1):466. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05839-0. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40170049 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ministry of Health. Regulation on large medical equipment allocation and utilization. 2004. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/cms-search/xxgk/getManuscriptXxgk.htm?id=40576. Accessed 1 Jan 2022.
-
- National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Notice on printing and distributing the “Guiding Opinions on National Class B High Technology Medical Equipment Allocation Planning”. 2005. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/wjw/gfxwj/201304/10047bb6587f4c2396e0848fd445fc58..... Accessed 1 Mar 2023.
-
- Lu J, Lv L, Cao Z, Zhao D. Ying X Access management strategy of large medical equipment based on government function reform and market development effect. Chin J Health Policy. 2017;10(08):55–59.
-
- Chen Z, Cause of public policy analysis. China city press 2004.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

