Enoxaparin sodium bone cement plays an anti-inflammatory immunomodulatory role by inducing the polarization of M2 macrophages
- PMID: 37221568
- PMCID: PMC10207791
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-023-03865-8
Enoxaparin sodium bone cement plays an anti-inflammatory immunomodulatory role by inducing the polarization of M2 macrophages
Abstract
Objective: The implantation of PMMA bone cement results in an immune response and the release of PMMA bone cement particles causes an inflammatory cascade. Our study discovered that ES-PMMA bone cement can induce M2 polarization of macrophages, which has an anti-inflammatory immunomodulatory effect. We also delved into the molecular mechanisms that underlie this process.
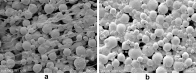
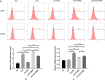
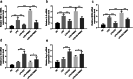
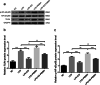
Methods: In this study, we designed and prepared samples of bone cement. These included PMMA bone cement samples and ES-PMMA bone cement samples, which were implanted into the back muscles of rats. At 3, 7, and 14 days after the operation, we removed the bone cement and a small amount of surrounding tissue. We then performed immunohistochemistry and immunofluorescence to observe the polarization of macrophages and the expression of related inflammatory factors in the surrounding tissues. The RAW264.7 cells were exposed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) for 24 h to establish the macrophage inflammation model. Then, each group was treated with enoxaparin sodium medium, PMMA bone cement extract medium, and ES-PMMA bone cement extract medium, respectively, and cultured for another 24 h. We collected cells from each group and used flow cytometry to detect the expressions of CD86 and CD206 in macrophages. Additionally, we performed RT-qPCR to determine the mRNA levels of three markers of M1 macrophages (TNF-α, IL-6, iNOS) and two M2 macrophage markers (Arg-1, IL-10). Furthermore, we analyzed the expression of TLR4, p-NF-κB p65, and NF-κB p65 through Western blotting.
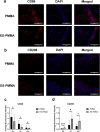
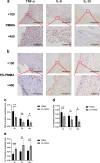
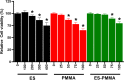
Results: The immunofluorescence results indicate that the ES-PMMA group exhibited an upregulation of CD206, an M2 marker, and a downregulation of CD86, an M1 marker, in comparison to the PMMA group. Additionally, the immunohistochemistry results revealed that the levels of IL-6 and TNF-α expression were lower in the ES-PMMA group than in the PMMA group, while the expression level of IL-10 was higher in the ES-PMMA group. Flow cytometry and RT-qPCR analyses revealed that the expression of M1-type macrophage marker CD86 was significantly elevated in the LPS group compared to the NC group. Additionally, M1-type macrophage-related cytokines TNF-α, IL-6, and iNOS were also found to be increased. However, in the LPS + ES group, the expression levels of CD86, TNF-α, IL-6, and iNOS were decreased, while the expression of M2-type macrophage markers CD206 and M2-type macrophage-related cytokines (IL-10, Arg-1) were increased compared to the LPS group. In comparison to the LPS + PMMA group, the LPS + ES-PMMA group demonstrated a down-regulation of CD86, TNF-α, IL-6, and iNOS expression levels, while increasing the expression levels of CD206, IL-10, and Arg-1. Western blotting results revealed a significant decrease in TLR4/GAPDH and p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65 in the LPS + ES group when compared to the LPS group. Additionally, the LPS + ES-PMMA group exhibited a decrease in TLR4/GAPDH and p-NF-κB p65/NF-κB p65 levels when compared to the LPS + PMMA group.
Conclusion: ES-PMMA bone cement is more effective than PMMA bone cement in down-regulating the expression of the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Additionally, it induces macrophages to polarize towards the M2 phenotype, making it a crucial player in anti-inflammatory immune regulation.
Keywords: Bone cement; Enoxaparin sodium; Inflammation; Macrophage.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This material has not been published and is not under consideration elsewhere. where. The authors declare that they have no competing interests. All authors have read and contributed to the submitted manuscript, and there is no conflict of interest among the authors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Novel composite bone cement modulates inflammatory response in vitro.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 14;15(1):8897. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93575-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40087513 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of Galectin-9/Tim-3 pathway on the polarization of M1/M2 subtype in murine macrophages induced by lipopolysaccharide].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Sep;30(9):836-841. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.09.004. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 30309408 Chinese.
-
Enoxaparin sodium bone cement displays local anti-inflammatory effects by regulating the expression of IL-6 and TNF-α.Heliyon. 2023 May 25;9(6):e16530. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16530. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37274684 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting different phenotypes of macrophages: A potential strategy for natural products to treat inflammatory bone and joint diseases.Phytomedicine. 2023 Sep;118:154952. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154952. Epub 2023 Jul 12. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 37506402 Review.
-
Modulation of M1 and M2 macrophage polarization by metformin: Implications for inflammatory diseases and malignant tumors.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 4;151:114345. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114345. Epub 2025 Mar 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40024215 Review.
Cited by
-
Biomechanical impact of enoxaparin sodium-chitosan-PMMA bone cement in hip arthroplasty: a preliminary finite element analysis.Front Surg. 2025 Jun 24;12:1615456. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2025.1615456. eCollection 2025. Front Surg. 2025. PMID: 40630863 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lncRNA NONMMUT104330.1-miR-709-DDX58 axis in mediating immunomodulatory effects of enoxaparin sodium bone cement on macrophage polarization and inflammatory response.J Orthop Surg Res. 2025 Aug 12;20(1):756. doi: 10.1186/s13018-025-06177-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2025. PMID: 40796855 Free PMC article.
-
Novel composite bone cement modulates inflammatory response in vitro.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 14;15(1):8897. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93575-4. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40087513 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

