Relationship Between Physical Activity and Adult Asthma Control Using NHANES 2011-2020 Data
- PMID: 37221818
- PMCID: PMC10226382
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.939350
Relationship Between Physical Activity and Adult Asthma Control Using NHANES 2011-2020 Data
Abstract
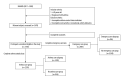
BACKGROUND The purpose of this study was to determine whether PA is associated with asthma control using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) for 2011-2020. We did not find a relationship between physical activity (PA) and asthma control. MATERIAL AND METHODS In this study, we measured asthma control by counting asthma attacks and emergency room visits for asthma in the past year. Physical activity was divided into recreational physical activity and work physical activity. A total of 3158 patients (≥20 years old) were included in the study, of which 2375 were in the asthma attack group and 2844 were in the emergency care group, with indicators of asthma control and physical activity as dichotomous variables. Multiple sets of covariates were selected, such as age, gender, and race. Multiple logistic regression analysis and subgroup analysis were used to analyze the data. RESULTS Active workload was significantly correlated with acute asthma attacks, but the relationship with emergency care was not statistically significant. We found that the relationship between physical activity and emergency care was influenced by race, education, and economic level. CONCLUSIONS The amount of work activity was correlated with acute asthma attacks, and the relationship between physical activity and emergency case was influenced by race, education, and economic level.
Conflict of interest statement
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous