ALTERNATIVE FISTULA RISK SCORE AND FIRST POSTOPERATIVE DAY DRAIN FLUID AMYLASE AS PREDICTORS OF PANCREATIC FISTULA AFTER PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY
- PMID: 37222385
- PMCID: PMC10202466
- DOI: 10.1590/0102-672020230002e1728
ALTERNATIVE FISTULA RISK SCORE AND FIRST POSTOPERATIVE DAY DRAIN FLUID AMYLASE AS PREDICTORS OF PANCREATIC FISTULA AFTER PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY
Abstract
Background: The high morbidity and mortality rates of pancreaticoduodenectomy are mainly associated with pancreaticojejunal anastomosis, the most fragile and susceptible to complications such as clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula.
Aims: The alternative fistula risk score and the first postoperative day drain fluid amylase are predictors of the occurrence of clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula. No consensus has been reached on which of the scores is a better predictor; moreover, their combined predictive power remains unclear. To the best of our knowledge, this association had not yet been studied.
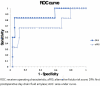
Methods: This study assessed the predictive effect of alternative fistula risk score and/or drain fluid amylase on clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula in a retrospective cohort of 58 patients following pancreaticoduodenectomy. The Shapiro-Wilk and Mann-Whitney tests were applied for assessing the distribution of the samples and for comparing the medians, respectively. The receiver operating characteristics curve and the confusion matrix were used to analyze the predictive models.
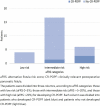
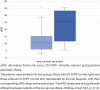
Results: The alternative fistula risk score values were not statistically different between patients in the clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula and non- clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula groups (Mann-Whitney U test 59.5, p=0.12). The drain fluid amylase values were statistically different between clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula and non- clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula groups (Mann-Whitney U test 27, p=0.004). The alternative fistula risk score and drain fluid amylase were independently less predictive for clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula, compared to combined alternative fistula risk score + drain fluid amylase.
Conclusion: The combined model involving alternative fistula risk score >20% + drain fluid amylase=5,000 U/L was the most effective predictor of clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula occurrence following pancreaticoduodenectomy.
RACIONAL:: A alta morbimortalidade da pancreaticoduodenectomia está associada, principalmente, à anastomose pancreatojejunal, a mais frágil e suscetível a complicações como a fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante (clinically relevant postoperative pancreatic fistula - CR-POPF).
OBJETIVOS:: O escore alternativo de risco de fístula (alternative fistula risk score) e os níveis de amilase do fluido de drenagem no primeiro dia pós-operatório (first postoperative day drain fluid) são preditores da ocorrência de fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante. Nenhum consenso foi alcançado sobre qual das pontuações é um melhor preditor; além disso, seu poder preditivo combinado permanece obscuro. Até onde sabemos, essa associação ainda não havia sido estudada.
MÉTODOS:: Este estudo avaliou o efeito preditivo do escore alternativo de risco de fístula e/ou do fluido de drenagem no primeiro dia pós-operatório em uma coorte retrospectiva de 58 pacientes após pancreaticoduodenectomia. Os testes de Shapiro-Wilk e Mann-Whitney foram aplicados para avaliar a distribuição das amostras e para comparar as medianas, respectivamente. A curva de características operacionais do receptor e a matriz de confusão foram utilizadas para analisar os modelos preditivos.
RESULTADOS:: Os valores do escore alternativo de risco de fístula não foram estatisticamente diferentes entre os pacientes dos grupos fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante e não- fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante (teste U de Mann-Whitney 59,5, p=0,12). Os valores de fluido de drenagem no primeiro dia pós-operatório foram estatisticamente diferentes entre os grupos fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante e não- fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante (teste U de Mann-Whitney 27, p=0,004). O escore alternativo de risco de fístula e fluido de drenagem no primeiro dia pós-operatório foram independentemente menos preditivos para fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante, em comparação com escore alternativo de risco de fístula + fluido de drenagem no primeiro dia pós-operatório combinados.
CONCLUSÕES:: O modelo combinado envolvendo escore alternativo de risco de fístula>20% + fluido de drenagem no primeiro dia pós-operatório=5.000 U/L foi o preditor mais eficaz da ocorrência de fístula pancreática pós-operatória clinicamente relevante após pancreaticoduodenectomia.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None.
Figures

References
-
- Correa-Gallego C, Brennan MF, D'angelica M, Fong Y, Dematteo RP, Kingham TP, Jarnagin WR, Allen PJ. Operative drainage following pancreatic resection: analysis of 1122 patients resected over 5 years at a single institution. Ann Surg. 2013;258(6):1051–1058. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3182813806. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

