Systemic Reprogramming of Endothelial Cell Signaling in Metastasis and Cachexia
- PMID: 37222464
- PMCID: PMC10281790
- DOI: 10.1152/physiol.00001.2023
Systemic Reprogramming of Endothelial Cell Signaling in Metastasis and Cachexia
Abstract
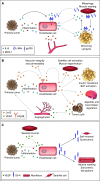
Proliferating cancer cells secrete a multitude of factors impacting metabolism, interorgan communication, and tumor progression. The distribution of tumor-derived factors to distant organs occurs via the circulation, which provides an extensive reactive surface lined by endothelial cells. Primary tumor-derived proteins impact cancer progression by modulating endothelial cell activation at the (pre-)metastatic niche, which affects tumor cell dissemination as well as the outgrowth of seeded metastatic cells into overt tumors. In addition, new insight indicates that endothelial cell signaling contributes to metabolic symptoms of cancer, including cancer-associated cachexia, opening a new field of vascular metabolism research. This review addresses how tumor-derived factors systemically affect endothelial cell signaling and activation and impact distant organs as well as tumor progression.
Keywords: angiocrine signaling; cachexia; metastasis; systemic signaling; vascular endothelium.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tumor Angiocrine Signaling: Novel Targeting Opportunity in Cancer.Cells. 2023 Oct 23;12(20):2510. doi: 10.3390/cells12202510. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37887354 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disturbed endothelial cell signaling in tumor progression and therapy resistance.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024 Feb;86:102287. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2023.102287. Epub 2023 Nov 28. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2024. PMID: 38029706 Review.
-
Endothelial Calcineurin Signaling Restrains Metastatic Outgrowth by Regulating Bmp2.Cell Rep. 2019 Jan 29;26(5):1227-1241.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2019.01.016. Cell Rep. 2019. PMID: 30699351
-
Targeting cancer cachexia: Molecular mechanisms and clinical study.MedComm (2020). 2022 Sep 10;3(4):e164. doi: 10.1002/mco2.164. eCollection 2022 Dec. MedComm (2020). 2022. PMID: 36105371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatic Endothelial Notch Activation Protects against Liver Metastasis by Regulating Endothelial-Tumor Cell Adhesion Independent of Angiocrine Signaling.Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 1;79(3):598-610. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1752. Epub 2018 Dec 10. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30530502
Cited by
-
Nanoparticles in tumor microenvironment remodeling and cancer immunotherapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2024 Apr 2;17(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13045-024-01535-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38566199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles in cancer cachexia: deciphering pathogenic roles and exploring therapeutic horizons.J Transl Med. 2024 May 27;22(1):506. doi: 10.1186/s12967-024-05266-9. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38802952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contemporaneous Perioperative Inflammatory and Angiogenic Cytokine Profiles of Surgical Breast, Colorectal, and Prostate Cancer Patients: Clinical Implications.Cells. 2023 Dec 4;12(23):2767. doi: 10.3390/cells12232767. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38067195 Free PMC article.
-
VEGF-induced Nrdp1 deficiency in vascular endothelial cells promotes cancer metastasis by degrading vascular basement membrane.Oncogene. 2024 Jun;43(24):1836-1851. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03038-9. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38654108
References
-
- Singhal M, Gengenbacher N, Abdul Pari AA, Kamiyama M, Hai L, Kuhn BJ, Kallenberg DM, Kulkarni SR, Camilli C, Preuss SF, Leuchs B, Mogler C, Espinet E, Besemfelder E, Heide D, Heikenwalder M, Sprick MR, Trumpp A, Krijgsveld J, Schlesner M, Hu J, Moss SE, Greenwood J, Augustin HG. Temporal multi-omics identifies LRG1 as a vascular niche instructor of metastasis. Sci Transl Med 13: eabe6805, 2021. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.abe6805. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bremnes RM, Dønnem T, Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Andersen S, Sirera R, Camps C, Marinez I, Busund LT. The role of tumor stroma in cancer progression and prognosis: emphasis on carcinoma-associated fibroblasts and non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 6: 209–217, 2011. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181f8a1bd. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

