Distinct Interaction Modes for the Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase Alpha-like Subunits
- PMID: 37222571
- PMCID: PMC10251799
- DOI: 10.1080/10985549.2023.2210023
Distinct Interaction Modes for the Eukaryotic RNA Polymerase Alpha-like Subunits
Abstract
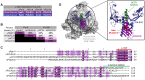
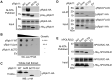
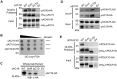
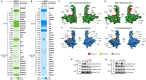
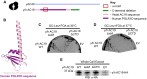
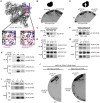
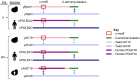
Eukaryotic DNA-dependent RNA polymerases (Pols I-III) encode two distinct alpha-like heterodimers where one is shared between Pols I and III, and the other is unique to Pol II. Human alpha-like subunit mutations are associated with several diseases including Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS), 4H leukodystrophy, and primary ovarian sufficiency. Yeast is commonly used to model human disease mutations, yet it remains unclear whether the alpha-like subunit interactions are functionally similar between yeast and human homologs. To examine this, we mutated several regions of the yeast and human small alpha-like subunits and used biochemical and genetic assays to establish the regions and residues required for heterodimerization with their corresponding large alpha-like subunits. Here we show that different regions of the small alpha-like subunits serve differential roles in heterodimerization, in a polymerase- and species-specific manner. We found that the small human alpha-like subunits are more sensitive to mutations, including a "humanized" yeast that we used to characterize the molecular consequence of the TCS-causingPOLR1D G52E mutation. These findings help explain why some alpha subunit associated disease mutations have little to no effect when made in their yeast orthologs and offer a better yeast model to assess the molecular basis of POLR1D associated disease mutations.
Keywords: AC19; POLR1D; POLR2J2; RNA polymerase; Rpb11; alpha subunits; homologs.
Figures
References
-
- Ishihama A. Subunit of assembly of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Adv Biophys. 1981;14:1–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
